Abstract
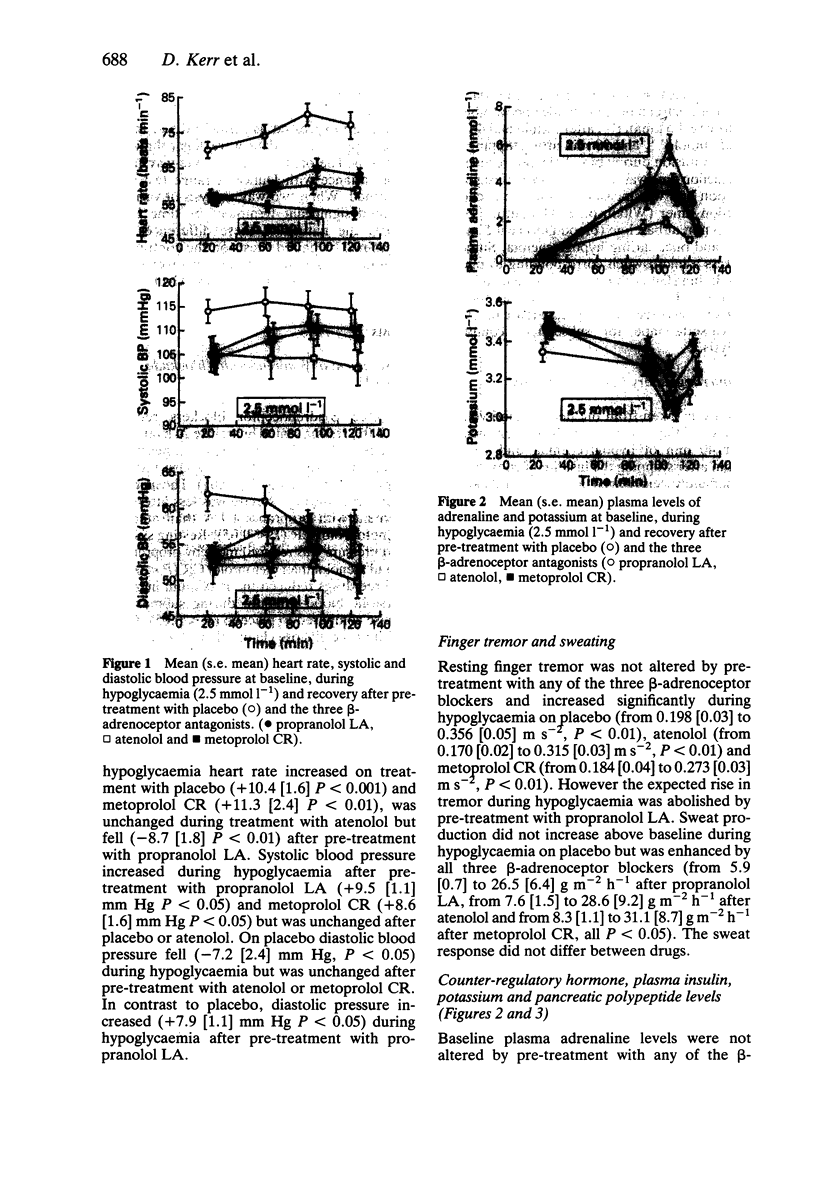
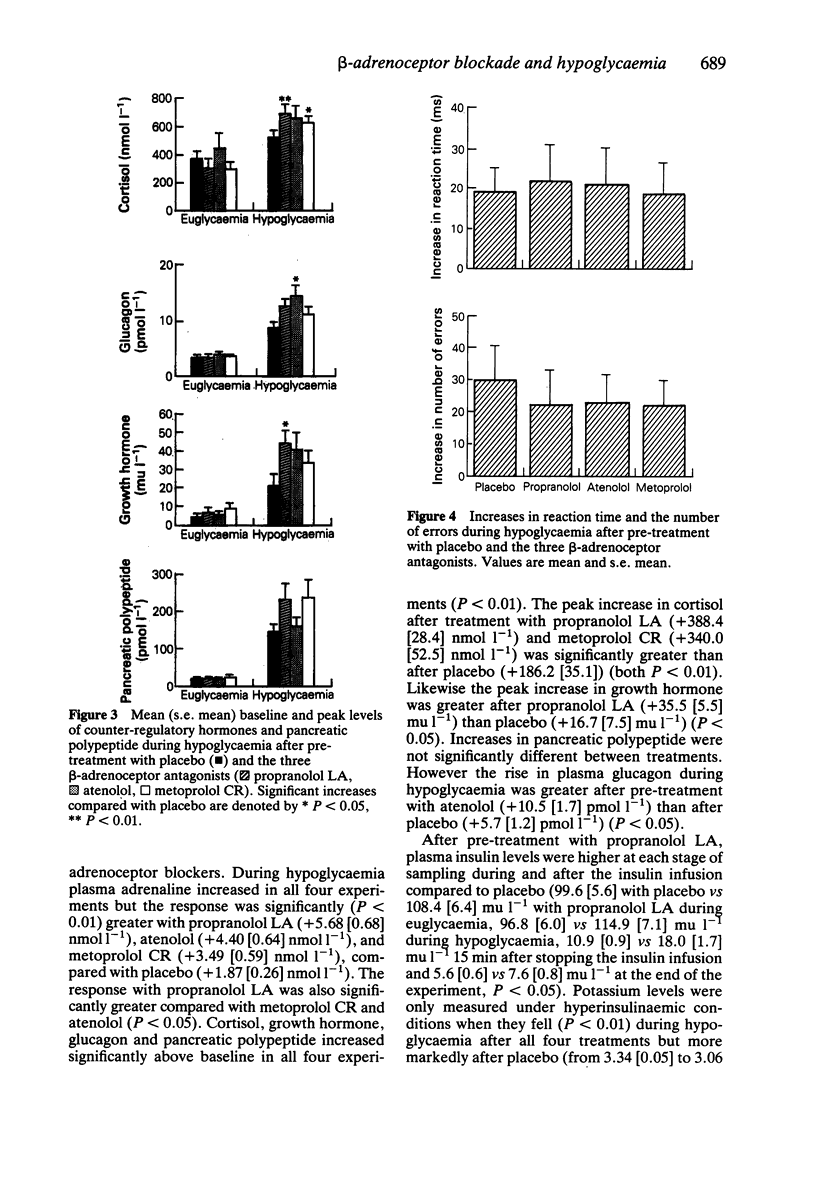
1. The effect of 1 week of treatment with propranolol LA (160 mg), atenolol (100 mg) and metoprolol CR (100 mg) on awareness of and the physiological responses to moderate hypoglycaemia were compared with placebo using a randomised, cross-over design in 12 healthy volunteers. 2. All three beta-adrenoceptor antagonists reduced resting heart rate, systolic blood pressure and heart rate responses to submaximal exercise compared with placebo. 3. Under hyperinsulinaemic (60 mu m-2 min-1) clamp conditions, at a blood glucose of 2.5 mmol l-1, atenolol prevented the rise in systolic and atenolol and metoprolol CR prevented the fall in diastolic blood pressure usually associated with hypoglycaemia. At this level of hypoglycaemia, the expected increase in heart rate was inhibited by atenolol but not metoprolol CR. Pre-treatment with propranolol LA resulted in a significant pressor response and a bradycardia during hypoglycaemia. In addition the normal increase in finger tremor was abolished by propranolol LA. 4. During hypoglycaemia all three beta-adrenoceptor blockers augmented sweating compared with placebo but hypoglycaemic symptoms, awareness and slowing of reaction time were the same with drugs and placebo. 5. The rise in plasma adrenaline and other counter-regulatory hormones during hypoglycaemia was enhanced by beta-adrenoceptor blockade. 6. We conclude that beta-adrenoceptor antagonists modify the physiological and hormonal responses to, but do not adversely affect awareness of, moderate hypoglycaemia in healthy volunteers.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abramson E. A., Arky R. A., Woeber K. A. Effects of propranolol on the hormonal and metabolic responses to insulin-induced hypoglycaemia. Lancet. 1966 Dec 24;2(7478):1386–1388. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(66)90422-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Altorfer R. M., Ziegler W. H., Froesch E. R. Insulin hypoglycaemia in normal and adrenalectomized subjects: comparison of metabolic parameters and endocrine counter regulation. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1981 Nov;98(3):413–419. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.0980413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackard W. G., Hubbell G. J. Stimulatory effect of exogenous catecholamines on plasma HGH concentrations in presence of beta adrenergic blockade. Metabolism. 1970 Jul;19(7):547–552. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(70)90010-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clausen-Sjöbom N., Lins P. E., Adamson U., Curstedt T., Hamberger B. Effects of metoprolol on the counter-regulation and recognition of prolonged hypoglycemia in insulin-dependent diabetics. Acta Med Scand. 1987;222(1):57–63. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1987.tb09929.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clutter W. E., Bier D. M., Shah S. D., Cryer P. E. Epinephrine plasma metabolic clearance rates and physiologic thresholds for metabolic and hemodynamic actions in man. J Clin Invest. 1980 Jul;66(1):94–101. doi: 10.1172/JCI109840. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corrall R. J., Frier B. M., Davidson N. M., Hopkins W. M., French E. B. Cholinergic manifestations of the acute autonomic reaction to hypoglycaemia in man. Clin Sci (Lond) 1983 Jan;64(1):49–53. doi: 10.1042/cs0640049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cryer P. E. Physiology and pathophysiology of the human sympathoadrenal neuroendocrine system. N Engl J Med. 1980 Aug 21;303(8):436–444. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198008213030806. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeFronzo R. A., Tobin J. D., Andres R. Glucose clamp technique: a method for quantifying insulin secretion and resistance. Am J Physiol. 1979 Sep;237(3):E214–E223. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1979.237.3.E214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deacon S. P., Barnett D. Comparison of atenolol and propranolol during insulin-induced hypoglycaemia. Br Med J. 1976 Jul 31;2(6030):272–273. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.6030.272. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deacon S. P., Karunanayake A., Barnett D. Acebutolol, atenolol, and propranolol and metabolic responses to acute hypoglycaemia in diabetics. Br Med J. 1977 Nov 12;2(6097):1255–1257. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.6097.1255. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRENCH E. B., KILPATRICK R. The role of adrenaline in hypoglycaemic reactions in man. Clin Sci. 1955 Nov;14(4):639–651. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster K. G., Haspineall J. R., Mollel C. L. Effects of propranolol on the response of human eccrine sweat glands to acetylcholine. Br J Dermatol. 1971 Oct;85(4):363–367. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.1971.tb14031.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerich J. E., Lorenzi M., Tsalikian E., Karam J. H. Studies on the mechanism of epinephrine-induced hyperglycemia in man. Evidence for participation of pancreatic glucagon secretion. Diabetes. 1976 Jan;25(1):65–71. doi: 10.2337/diab.25.1.65. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HALES C. N., RANDLE P. J. Immunoassay of insulin with insulin-antibody precipitate. Biochem J. 1963 Jul;88:137–146. doi: 10.1042/bj0880137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heller S. R., Macdonald I. A., Herbert M., Tattersall R. B. Influence of sympathetic nervous system on hypoglycaemic warning symptoms. Lancet. 1987 Aug 15;2(8555):359–363. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(87)92382-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerr D., Macdonald I. A., Tattersall R. B. Adaptation to mild hypoglycaemia in normal subjects despite sustained increases in counter-regulatory hormones. Diabetologia. 1989 Apr;32(4):249–254. doi: 10.1007/BF00285293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lager I., Blohmé G., Smith U. Effect of cardioselective and non-selective beta-blockade on the hypoglycaemic response in insulin-dependent diabetics. Lancet. 1979 Mar 3;1(8114):458–462. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(79)90821-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lager I., Jagenburg R., von Schenck H., Smith U. Effect of beta-blockade on hormone release during hypoglycaemia in insulin-dependent diabetics. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1980 Nov;95(3):364–371. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.0950364. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macdonald I. A., Lake D. M. An improved technique for extracting catecholamines from body fluids. J Neurosci Methods. 1985 May;13(3-4):239–248. doi: 10.1016/0165-0270(85)90072-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsden C. D., Foley T. H., Owen D. A., McAllister R. G. Peripheral beta-adrenergic receptors concerned with tremor. Clin Sci. 1967 Aug;33(1):53–65. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newman R. J. Comparison of propranolol, metoprolol, and acebutolol on insulin-induced hypoglycaemia. Br Med J. 1976 Aug 21;2(6033):447–449. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.6033.447. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Hare M. M., Daly J. G., Buchanan K. D. Radioimmunoassay for pancreatic polypeptide, and its age-related changes in concentration. Clin Chem. 1983 Nov;29(11):1923–1927. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogle C. W., Turner P., Markomihelakis H. The effects of high doses of oxprenolol and of propranolol on pursuit rotor performance, reaction time and critical flicker frequency. Psychopharmacologia. 1976 Apr 15;46(3):295–299. doi: 10.1007/BF00421117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ostman J., Arner P., Haglund K., Juhlin-Dannfelt A., Nowak J., Wennlund A. Effect of metoprolol and alprenolol on the metabolic, hormonal, and haemodynamic response to insulin-induced hypoglycaemia in hypertensive, insulin-dependent diabetics. Acta Med Scand. 1982;211(5):381–385. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1982.tb01966.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Popp D. A., Tse T. F., Shah S. D., Clutter W. E., Cryer P. E. Oral propranolol and metoprolol both impair glucose recovery from insulin-induced hypoglycemia in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care. 1984 May-Jun;7(3):243–247. doi: 10.2337/diacare.7.3.243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pramming S., Thorsteinsson B., Theilgaard A., Pinner E. M., Binder C. Cognitive function during hypoglycaemia in type I diabetes mellitus. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1986 Mar 8;292(6521):647–650. doi: 10.1136/bmj.292.6521.647. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saunders J., Gomeni R., Kilborn J. R., Morselli P. L., Sönksen P. H. A comparison between propranolol, practolol and betaxolol (SL75212) on the circulatory and metabolic responses to insulin-induced hypoglycaemia. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 1981;21(3):177–184. doi: 10.1007/BF00627917. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlüter K. J., Aellig W. H., Petersen K. G., Rieband H. C., Wehrli A., Kerp L. The influence of beta-adrenoceptor blocking drugs with and without intrinsic sympathomimetic activity on the hormonal responses to hypo- and hyperglycaemia. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1982;13(Suppl 2):407S–417S. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1982.tb01948.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith U., Blohmé G., Lager I., Lönnroth P. Can insulin-treated diabetics be given beta-adrenergic-blocking drugs? Br Med J. 1980 Oct 25;281(6248):1143–1144. doi: 10.1136/bmj.281.6248.1143-a. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens A. B., McKane W. R., Bell P. M., Bell P., King D. J., Hayes J. R. Psychomotor performance and counterregulatory responses during mild hypoglycemia in healthy volunteers. Diabetes Care. 1989 Jan;12(1):12–17. doi: 10.2337/diacare.12.1.12. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stout R. W., Henry R. W., Buchanan K. D. Triglyceride metabolism in acute starvation: the role of secretin and glucagon. Eur J Clin Invest. 1976 Mar 31;6(2):179–185. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.1976.tb00509.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor A. L., Fishman L. M. Corticotropin-releasing hormone. N Engl J Med. 1988 Jul 28;319(4):213–222. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198807283190405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Viberti G. C., Keen H., Bloom S. R. Beta blockade and diabetes mellitus: effect of oxprenolol and metoprolol on the metabolic, cardiovascular, and hormonal response to insulin-induced hypoglycemia in normal subjects. Metabolism. 1980 Sep;29(9):866–872. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(80)90126-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waal-Manning H. J. Can beta-blockers be used in diabetic patients? Drugs. 1979 Mar;17(3):157–160. doi: 10.2165/00003495-197917030-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilcox R. G., Bennett T., Macdonald I. A., Herbert M., Skene A. M. The effects of acute or chronic ingestion of propranolol or metoprolol on the physiological responses to prolonged, submaximal exercise in hypertensive men. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1984 Mar;17(3):273–281. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1984.tb02342.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Rooy P., Myburgh D. P., Cilliers A. J. Evaluation of the effect of atenolol on the reaction time of healthy volunteers. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 1985;28 (Suppl):105–107. doi: 10.1007/BF00543721. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


