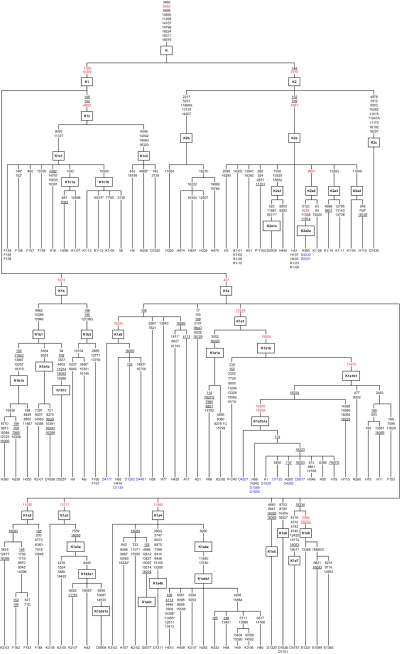
Figure 1.
Most parsimonious tree of complete Hg K mtDNA sequences. The tree is rooted in Hg U* and includes 121 mtDNAs, of which 28 are novel and 93 were reported elsewhere (12 sequences from Finnila et al. [2001], 1 from Maca-Meyer et al. [2001], 47 from Herrnstadt et al. [2002] [including the control-region information that was not reported], 1 from Mishmar et al. [2003], 28 from Coble et al. [2004], 2 from Palanichamy et al. [2004], and 2 from Achilli et al. [2005]). The genotyping information from Finnila et al. (2001) included herein corrects several inaccuracies that were reported elsewhere for the control-region phylogeny. Mutations are shown on the branches and are transitions unless the base change is explicitly indicated. Deletions are indicated by a “D” following the deleted nucleotide position. Insertions are indicated by a dot followed by the number and type of inserted nucleotide(s). Underlined nucleotide positions occur at least twice in the tree. An asterisk (*) at the end of a nucleotide position denotes a reversion. The information of the reported samples is presented in table 3. Samples in blue are from Ashkenazi Jews. Nucleotide positions in red were assayed in the entire set of 789 mtDNAs belonging to K. To resolve three possible reticulations, reversions at nucleotide 7082 in sample A01 and nucleotides 10398 and 11485 in sample H510 and a homoplasy at nucleotide 7927 for subHg K1a1a and K1a8 were assumed. The tree was drawn by hand from networks constructed using program Network 4.1.0.0. We applied the reduced-median algorithm (ρ=2) followed by the median-joining algorithm (ε=2), as described at the Fluxus Engineering Web site. The control-region positions were twofold down-weighted, with respect to coding-region positions. The hypervariable nucleotides 16182 and 16183 in HVS-I and the indels at nucleotides 309, 315, and 524 in HVS-II were excluded. Coding-region mutations at nucleotides 750, 1438, 1811, 2706, 4769, 7028, 8860, 11467, 11719, and 12308 are not shown unless reverted. Ethnic designation of the sequences was available for the sequences reported by Finnila et al. (2001), Maca-Meyer et al. (2001), Palanichamy et al. (2004), and Achilli et al. (2005), and for the novel samples reported herein (table 3).