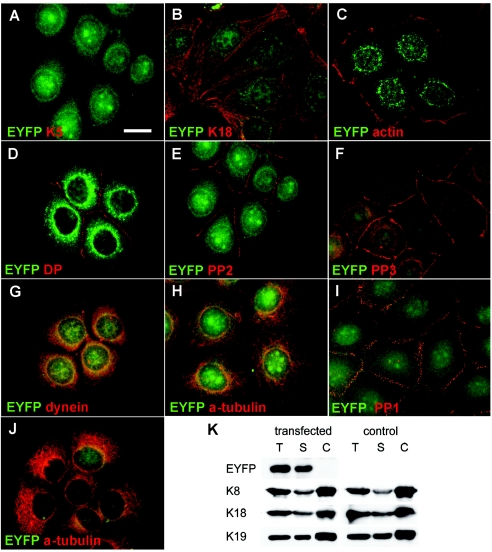
Figure 5.
Immunofluorescence and biochemical analysis of transfected MCF-7 and HaCaT cells stably expressing an EYFP-p.Ile140fs fusion protein. A and B, MCF-7 cells showing random distribution of the K5 head domain throughout transfectants, including nuclei. Staining for K18, representative of endogenous keratins, revealed no colocalization of EYFP-p.Ile140fs with endogenous keratins (B). Stably transfected MCF-7 cells are stained with antibodies against actin (C), desmoplakin (DP) (D), plakophilin 2 (PP2) (E), and plakophilin 3 (PP3) (F). Stably transfected HaCaT keratinocytes are stained with antibodies against plakophilin 1 (PP1) (I) and α-tubulin (J). In both cell lines, no colocalization or altered distribution between EYFP-p.Ile140fs and any of these proteins was detected. In MCF-7 cells, a partial colocalization of EYFP-p.Ile140fs (yellow overlay) with dynein intermediate chain (G), but not with α-tubulin (H), was detected. Fractionation and immunoblotting of MCF-7 cells stably transfected with EYFP-p.Ile140fs and mock-transfected controls (K). Blots containing total (T), soluble (S), and Triton/high-salt–insoluble cytoskeletal proteins (C) were incubated with antibodies against EYFP, K8, K18, and K19. EYFP-p.Ile140fs was detected exclusively in the soluble fraction harvested from transfected MCF-7 cells, without affecting the solubility of endogenous keratins. Scale bar represents 20 μm.