Abstract
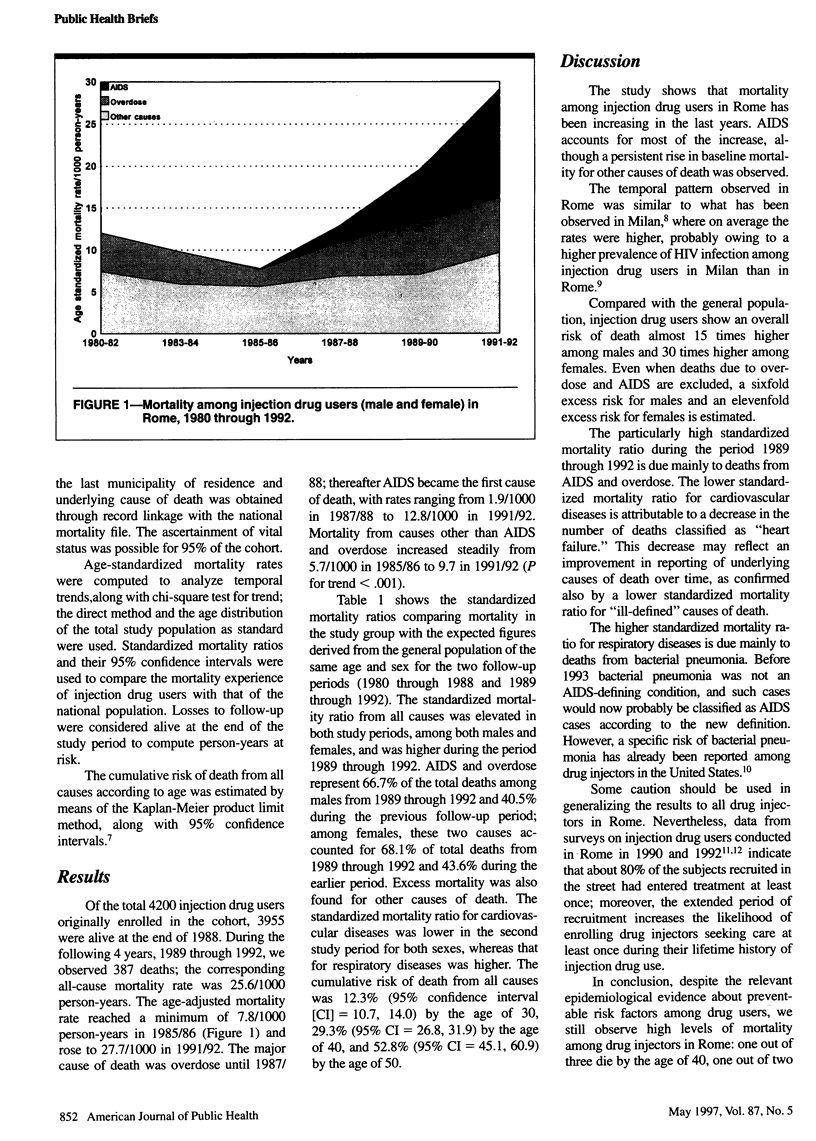
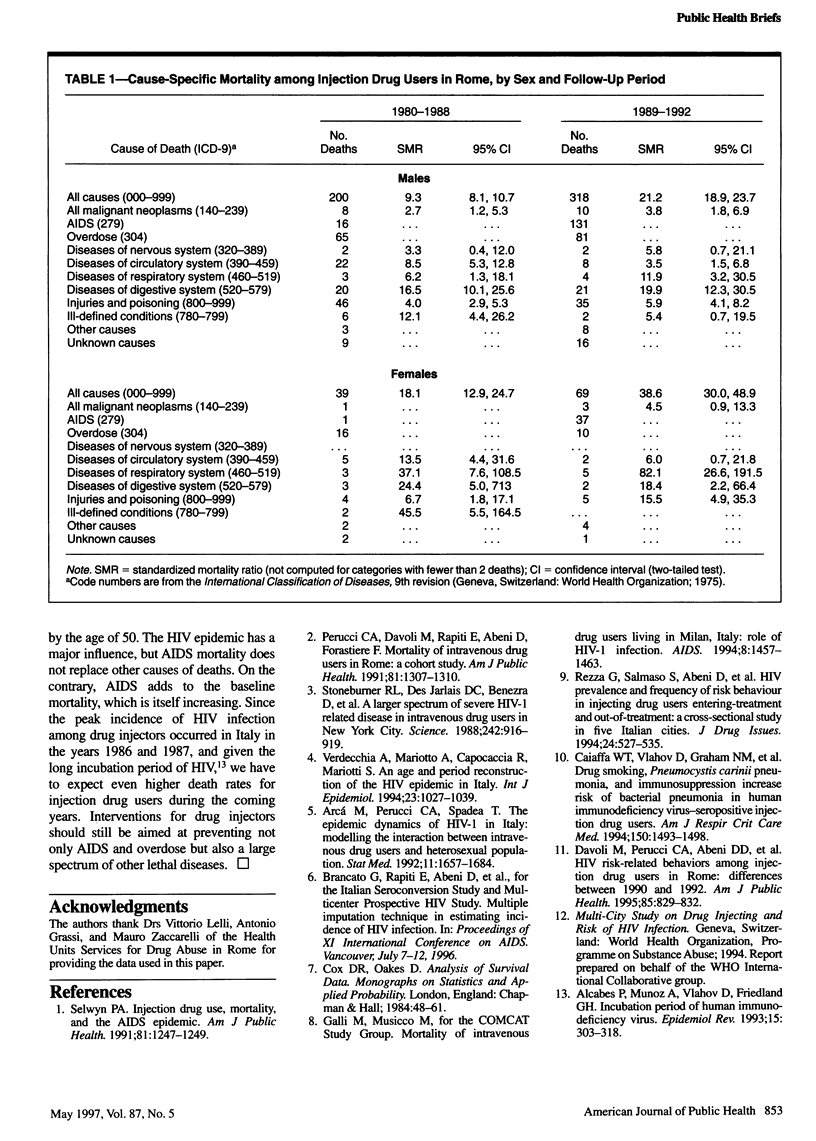
OBJECTIVES: The purpose of the study was to analyze overall and cause-specific mortality among injection drug users in Rome. METHODS: A cohort of 4200 injection drug users was enrolled in drug treatment centers from 1980 through 1988 and followed up until December 1992. RESULTS: The age-adjusted mortality rate from all causes increased from 7.8/1000 person-years in 1985/86 to 27.7/1000 in 1991/92. The rise was mainly attributable to acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS), but mortality from overdose and other causes increased as well. The cumulative risk of death by the age of 40 was 29.3%. CONCLUSIONS: The impact of AIDS deaths appears to be additional to a persistent increase of mortality for all other causes.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alcabes P., Muñoz A., Vlahov D., Friedland G. H. Incubation period of human immunodeficiency virus. Epidemiol Rev. 1993;15(2):303–318. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.epirev.a036122. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arcà M., Perucci C. A., Spadea T. The epidemic dynamics of HIV-1 in Italy: modelling the interaction between intravenous drug users and heterosexual population. Stat Med. 1992 Sep 30;11(13):1657–1684. doi: 10.1002/sim.4780111303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caiaffa W. T., Vlahov D., Graham N. M., Astemborski J., Solomon L., Nelson K. E., Muñoz A. Drug smoking, Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia, and immunosuppression increase risk of bacterial pneumonia in human immunodeficiency virus-seropositive injection drug users. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1994 Dec;150(6 Pt 1):1493–1498. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm.150.6.7952605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davoli M., Perucci C. A., Abeni D. D., Arcà M., Brancato G., Forastiere F., Montiroli P. M., Zampieri F. HIV risk-related behaviors among injection drug users in Rome: differences between 1990 and 1992. Am J Public Health. 1995 Jun;85(6):829–832. doi: 10.2105/ajph.85.6.829. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galli M., Musicco M. Mortality of intravenous drug users living in Milan, Italy: role of HIV-1 infection. COMCAT Study Group. AIDS. 1994 Oct;8(10):1457–1463. doi: 10.1097/00002030-199410000-00013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perucci C. A., Davoli M., Rapiti E., Abeni D. D., Forastiere F. Mortality of intravenous drug users in Rome: a cohort study. Am J Public Health. 1991 Oct;81(10):1307–1310. doi: 10.2105/ajph.81.10.1307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selwyn P. A. Injection drug use, mortality, and the AIDS epidemic. Am J Public Health. 1991 Oct;81(10):1247–1249. doi: 10.2105/ajph.81.10.1247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoneburner R. L., Des Jarlais D. C., Benezra D., Gorelkin L., Sotheran J. L., Friedman S. R., Schultz S., Marmor M., Mildvan D., Maslansky R. A larger spectrum of severe HIV-1--related disease in intravenous drug users in New York City. Science. 1988 Nov 11;242(4880):916–919. doi: 10.1126/science.3187532. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verdecchia A., Mariotto A., Capocaccia R., Mariotti S. An age and period reconstruction of the HIV epidemic in Italy. Int J Epidemiol. 1994 Oct;23(5):1027–1039. doi: 10.1093/ije/23.5.1027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


