Abstract
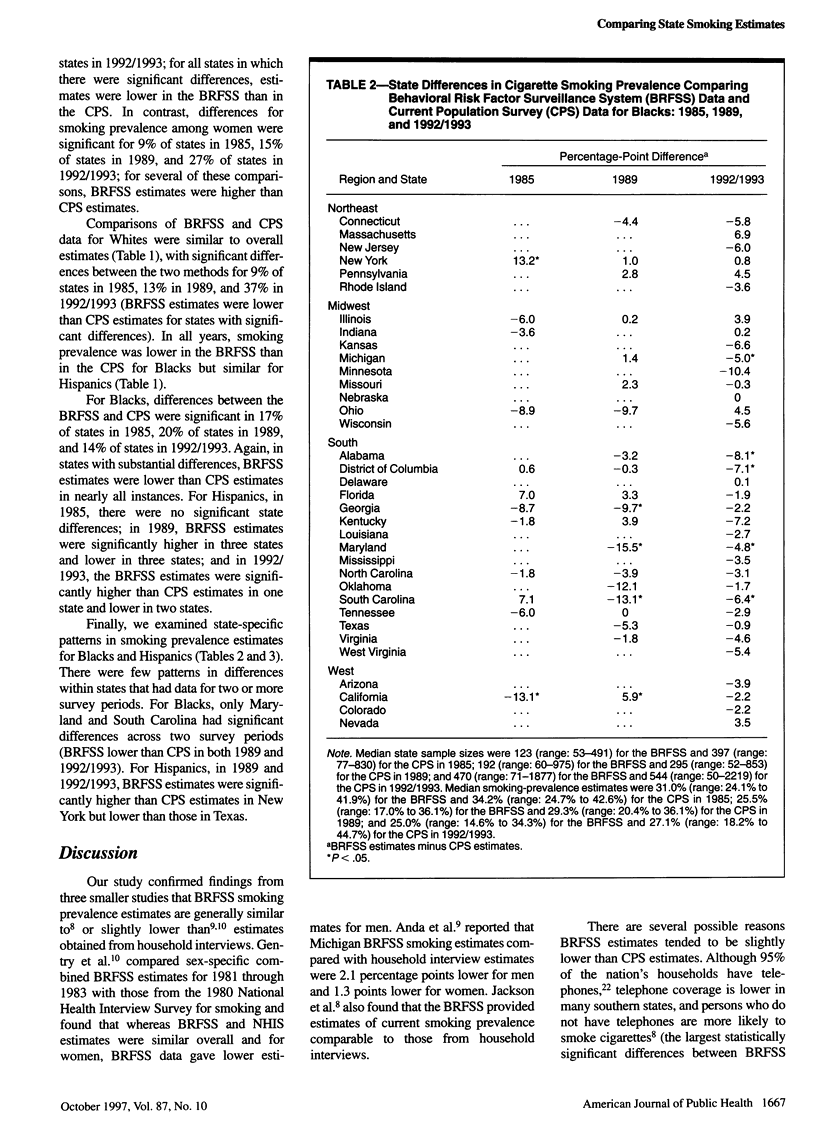
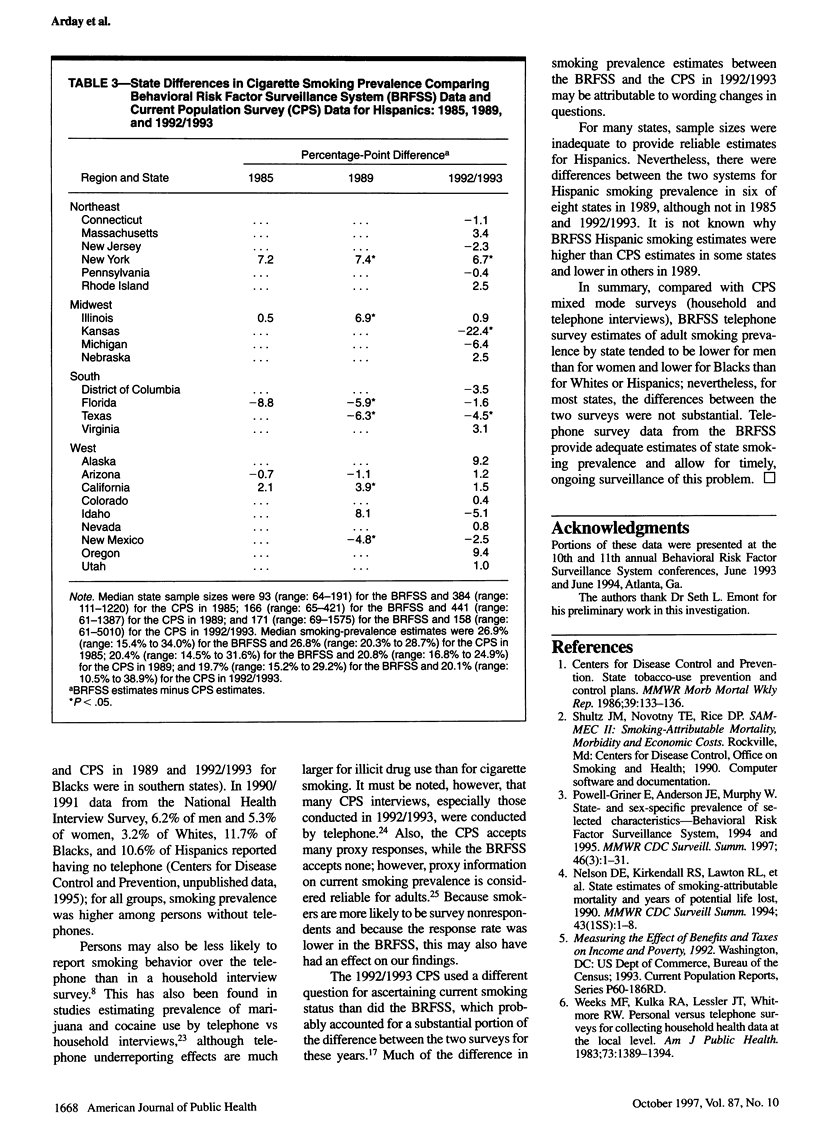
OBJECTIVES: This study examined whether there are systematic differences between the Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System (BRFSS) and the Current Population Survey (CPS) for state cigarette smoking prevalence estimates. METHODS: BRFSS telephone survey estimates were compared with estimates from the US Census CPS tobacco-use supplements (the CPS sample frame includes persons in households without telephones). Weighted overall and sex- and race-specific BRFSS and CPS state estimates of adults smoking were analyzed for 1985, 1989, and 1992/1993. RESULTS: Overall estimates of smoking prevalence from the BRFSS were slightly lower than estimates from CPS (median difference: -2.0 percentage points in 1985, -0.7 in 1989, and -1.9 in 1992/1993; P < .05 for all comparisons), but there was variation among states. Differences between BRFSS and CPS estimates were larger among men than among women and larger among Blacks than among Hispanics or Whites; for most states, these differences were not significant. CONCLUSIONS: The BRFSS generally provides state estimates of smoking prevalence similar to those obtained from CPS, and these are appropriate for ongoing state surveillance of smoking prevalence.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Gentry E. M., Kalsbeek W. D., Hogelin G. C., Jones J. T., Gaines K. L., Forman M. R., Marks J. S., Trowbridge F. L. The behavioral risk factor surveys: II. Design, methods, and estimates from combined state data. Am J Prev Med. 1985 Nov-Dec;1(6):9–14. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson C., Jatulis D. E., Fortmann S. P. The Behavioral Risk Factor Survey and the Stanford Five-City Project Survey: a comparison of cardiovascular risk behavior estimates. Am J Public Health. 1992 Mar;82(3):412–416. doi: 10.2105/ajph.82.3.412. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLaughlin J. K., Dietz M. S., Mehl E. S., Blot W. J. Reliability of surrogate information on cigarette smoking by type of informant. Am J Epidemiol. 1987 Jul;126(1):144–146. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a114647. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson D. E., Kirkendall R. S., Lawton R. L., Chrismon J. H., Merritt R. K., Arday D. A., Giovino G. A. Surveillance for smoking-attributable mortality and years of potential life lost, by state--United States, 1990. MMWR CDC Surveill Summ. 1994 Jun 10;43(1):1–8. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powell-Griner E., Anderson J. E., Murphy W. State-and sex-specific prevalence of selected characteristics--behavioral risk factor surveillance system, 1994 and 1995. MMWR CDC Surveill Summ. 1997 Aug 1;46(3):1–31. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Remington P. L., Smith M. Y., Williamson D. F., Anda R. F., Gentry E. M., Hogelin G. C. Design, characteristics, and usefulness of state-based behavioral risk factor surveillance: 1981-87. Public Health Rep. 1988 Jul-Aug;103(4):366–375. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegel P. Z., Frazier E. L., Mariolis P., Brackbill R. M., Smith C. Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance, 1991: monitoring progress toward the nation's year 2000 health objectives. MMWR CDC Surveill Summ. 1993 Aug 27;42(4):1–21. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treviño F. M., Moyer M. E., Valdez R. B., Stroup-Benham C. A. Health insurance coverage and utilization of health services by Mexican Americans, mainland Puerto Ricans, and Cuban Americans. JAMA. 1991 Jan 9;265(2):233–237. doi: 10.1001/jama.1991.03460020087034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weeks M. F., Kulka R. A., Lessler J. T., Whitmore R. W. Personal versus telephone surveys for collecting household health data at the local level. Am J Public Health. 1983 Dec;73(12):1389–1394. doi: 10.2105/ajph.73.12.1389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


