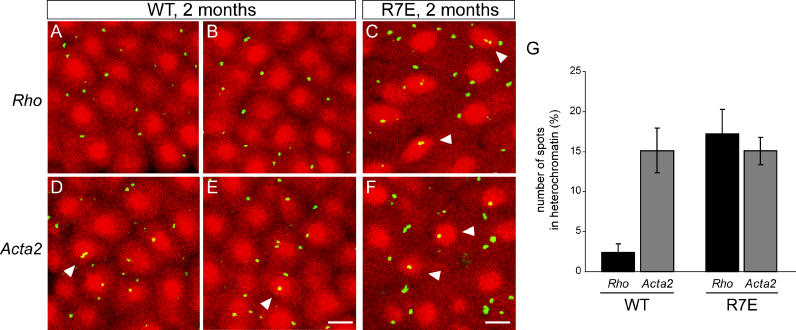
Figure 5. Loss of a Specific Gene Compartmentalization in Rods from SCA7 Mice.
(A–F) BAC probes containingRho (A–C) orActa2 (D–F) genes were hybridized to retinal cryosections from 2-mo-old WT (A), (B), (D), and (E) or R7E (C) and (F) animals. FISH signals appear in green whereas DAPI-stained photoreceptor nuclei were pseudo-colored in red for better visualization. Merged images were collected by confocal imaging analysis and showed co-localization ofActa2 within the densely DAPI-stained heterochromatin region in WT rod nuclei (arrowheads in [D] and [E]). By contrast,Rho was excluded from this compact heterochromatin region. In R7E rod nuclei,Rho andActa2 showed a comparable random pattern of intranuclear distribution. Both could be found co-localizing within the central densely DAPI-stained region (arrowheads in [C] and [F]). Scale bars represent 2 μm.
(G) Distribution ofRho andActa2 between heterochromatin and euchromatin territories in WT and R7E rod nuclei was estimated by counting the number of spots detected in the densely DAPI-stained region. Counting was performed on the projection of four consecutivez stacks (1.2 μm between each stack) taken through the retinal section such that only entire rod nuclei were included in the counting. More than 500 nuclei were analyzed, and each bar represents the mean value ± SEM of three independent experiments performed on two different animals.