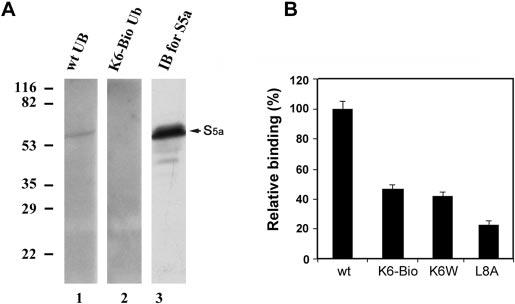
FIG. 5.
Conjugates formed with Lys6-modified ubiquitin bind S5a of the proteasome with reduced avidity. Ubiquitin conjugates of α-lactalbumin were formed with wild-type, Lys6-biotinylated, or K6W or L8A mutant ubiquitin and isolated as described in the legend to Fig. 4. A, proteasome isolated from rabbit reticulocytes was resolved by SDS-PAGE and transferred to polyvinylidene difluoride membranes. After denaturation and renaturation procedures, the membranes were incubated overnight with conjugates of 125I-labeled α-lactalbumin formed with wild-type or Lys6-biotinylated ubiquitin. After removal of nonspecifically bound radioactivity, the membranes were exposed to x-ray film, and the specific binding was visualized by autoradiography. Lane 1, conjugates formed with wild-type ubiquitin (wt UB); lane 2, conjugates formed with Lys6-biotinylated ubiquitin (K6-Bio Ub); lane 3, Western blot analysis (immunoblotting (IB)) of the 26 S proteasome using antibody to S5a. B, shown are the results from S5a binding assay. Equal amounts of ubiquitinated 125I-labeled α-lactalbumin (4 × 104 cpm) formed with wild-type, Lys6-biotinylated, or K6W or L8A mutant ubiquitin were incubated with GST-S5a, which was immobilized overnight on glutathione-agarose beads with constant shaking. After extensive washing, ubiquitin conjugates were eluted from the beads with glutathione and quantified using a γ-counter. The data presented are the relative binding capabilities, where the binding capability of conjugates formed with wild-type ubiquitin is designated as 100%.