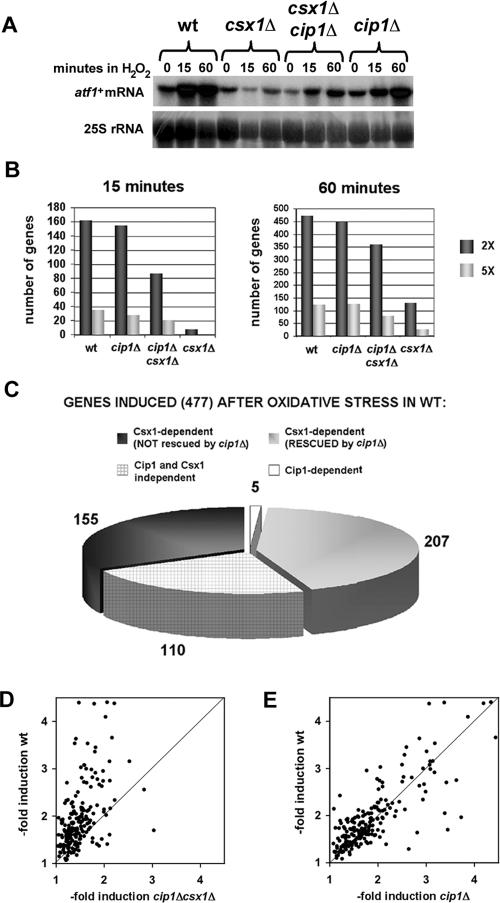
Figure 4.
Influence of Cip1 on global gene expression after oxidative stress. (A) Northern blot of atf1+ mRNA before (time 0) and after treatment of wild-type, csx1Δ, cip1Δ, and cip1Δ csx1Δ cells with 1 mM H2O2 for 15 or 60 min. 25S rRNA is shown as loading control. (B) Comparison of the total number of genes with two- or fivefold induction in wild-type, cip1Δ, cip1Δ csx1Δ, or csx1Δ cells 15 and 60 min after treatment with 1 mM H2O2. (C) Role of Cip1 and Csx1 in controlling the expression of genes induced at least twofold at one or both time-points (15 and/or 60 min) in wild-type cells. (D and E) Scatter chart analyses of the induction levels of the genes shown in Figure 4B as Csx1-dependent (RESCUED by cip1Δ). Comparisons were made between wild-type cells and cip1Δ csx1Δ mutants (D) or wild-type and cip1Δ cells (E).