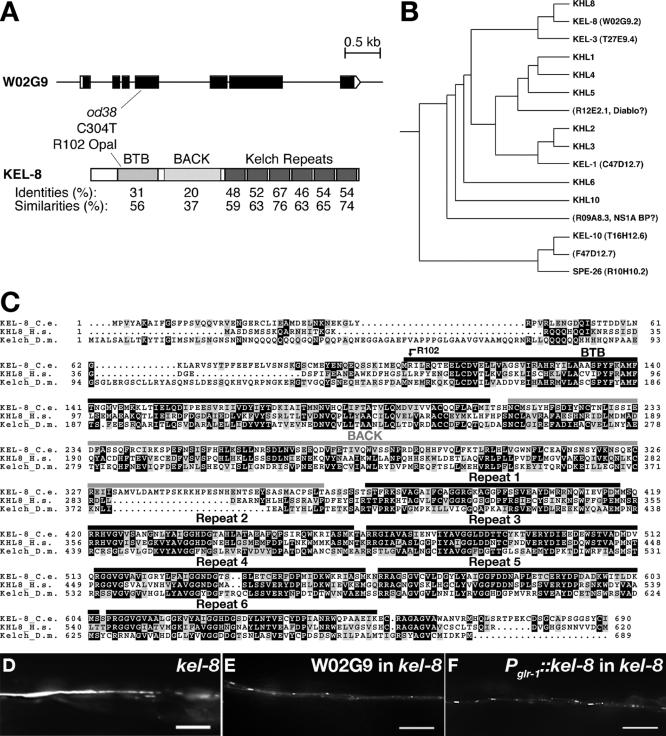
Figure 2.
KEL-8 encodes a member of the Kelch Superfamily. (A) The predicted intron/exon gene structure of kel-8 based on cDNA sequence is shown at top. Black boxes indicate coding sequences, whereas white boxes indicate untranslated regions. At bottom is the predicted protein domain structure, including the BTB, BACK, and six Kelch repeats. Amino acid identities and similarities to human Kelch-like 8 (KHL8) for each domain are shown. The molecular nature of the od38 mutation is indicated. (B) Phylogenetic tree for KEL-8 and various Kelch proteins in the human and C. elegans genomes. KEL-8 is most similar to human Kelch-like 8. (C) Amino acid alignment of KEL-8, human KHL8, and Drosophila KELCH. Black highlighting indicates identities, and gray highlighting indicates similarities. Overlines indicate specific protein domains. (D) Fluorescence from GLR-1::GFP in the ventral cord bundle of kel-8 mutants. (E) kel-8 mutants rescued with genomic cosmid W02G9 containing the kel-8 locus. (F) kel-8 mutants rescued cell autonomously with a Pglr-1::kel-8 transgene containing wild-type kel-8 cDNA fused to the glr-1 promoter. Bar, 5 μm.