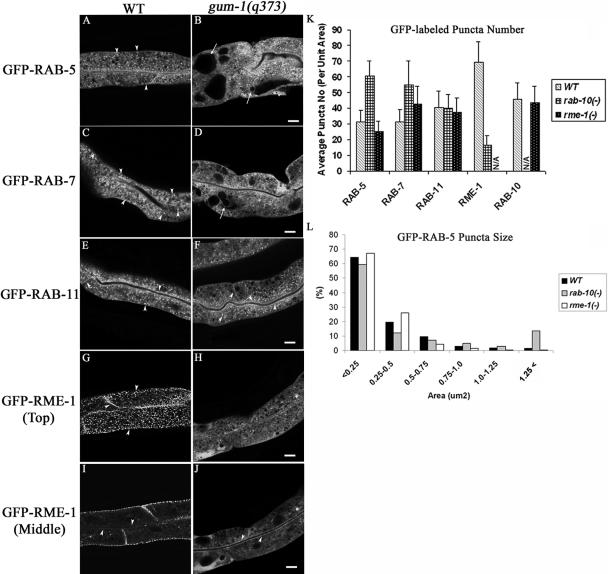
Figure 2.
gum-1 mutants accumulate endosomes marked with GFP-RAB-5 and GFP-RAB-7 and lose most endosomes marked with GFP-RME-1. Confocal images in a wild-type background are shown for GFP-RAB-5 (A), GFP-RAB-7 (C), GFP-RAB11 (E), or GFP-RME-1 (G and I). Confocal images in a gum-1(q373) background are shown for GFP-RAB-5 (B), GFP-RAB-7 (D), GFP-RAB11 (F), or GFP-RME-1 (H and J). Similar defects were found in gum-1(dx2) mutants (unpublished data). Arrowheads indicate punctate, tubular, or ringlike endosomes labeled by GFP-RAB-5, GFP-RAB-7, GFP-RAB-11, and GFP-RME-1 in the apical, cytosolic, lateral, or basolateral compartments. Arrows indicate enlarged intestinal endosomes (vacuoles) labeled by GFP-RAB-5 (B) or GFP-RAB-7 (D). Quantification of endosome number as visualized by the markers is shown in K. Error bars represent standard deviations from the mean (n = 24 each, 8 animals of each genotype sampled in three different regions of each intestine). Quantification of GFP-RAB-5-positive endosome size is graphed in L. Bar, 10 μm.