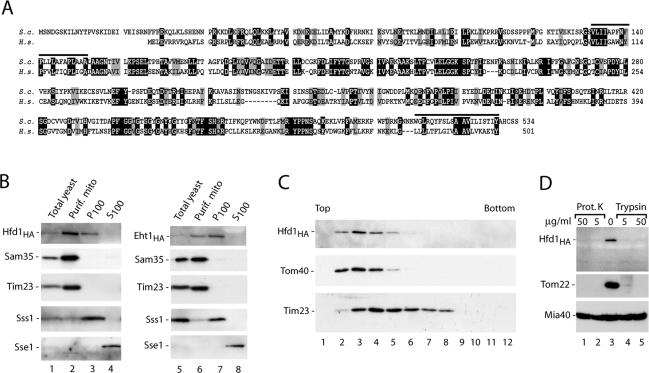
Figure 3.
The homologue of human fatty aldehyde dehydrogenase is mainly located in the mitochondrial outer membrane. (A) Comparison of the predicted primary structures of S. cerevisiae Hfd1, encoded by the open reading frame YMR110c (S.c.), and the human fatty aldehyde dehydrogenase FALDH (H.s.). Black, identical residues; gray, similar residues; bars, predicted hydrophobic transmembrane segments found by the HMMTOP program (Tusnady and Simon, 2001). (B) Subcellular fractionation of yeast strains, containing HA-tagged versions of Hfd1 or Eht1 (Open Biosystems, Brussels, Belgium), according to Meisinger et al. (2000), followed by SDS-PAGE and Western blot analysis. Equal amounts of proteins were loaded. The mitochondrial fraction was purified by sucrose gradient purification. P100, S100, pellet, and supernatant of 100,000 × g centrifugation. Sss1, subunit of the Sec61 protein translocase (endoplasmic reticulum); Sse1, cytosolic heat-shock protein 70. (C) Hfd1HA is located in the outer membrane. Separation of outer and inner membrane vesicles from Hfd1HA mitochondria on a sucrose gradient was performed as described in Materials and Methods. Fractions were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and immunodecoration using antisera against HA, the outer membrane protein Tom40, and the inner membrane protein Tim23. (D) Mitochondrial Hfd1 is accessible to proteases. Highly purified mitochondria (50 μg of protein) isolated from the Hfd1HA strain were resuspended in 100 μl of SEM buffer containing either proteinase K or trypsin and incubated for 15 min on ice. Proteinase K was inhibited by adding 2 mM PMSF, and trypsin was blocked by a 30-fold excess of soybean pancreatic trypsin inhibitor. After washing with SEM, mitochondria were separated on SDS-PAGE and analyzed by Western blotting and immunodecoration.