Figure 7.
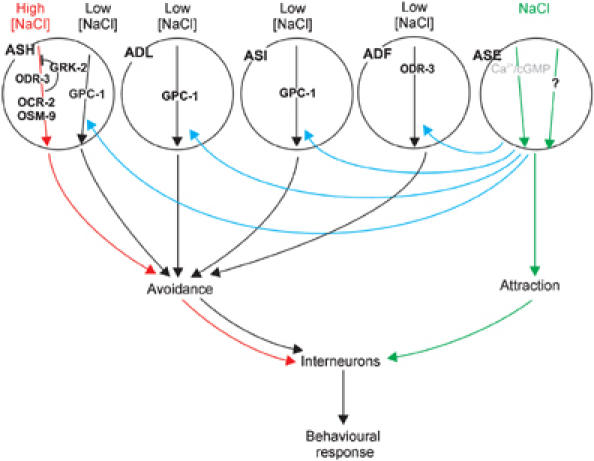
Model for NaCl detection and its plasticity in C. elegans. NaCl is detected by the ASE sensory neurons (green arrows), probably using cGMP/Ca2+ signalling and an unknown signalling pathway. Attraction is antagonised by avoidance mediated by the ASH neurons (red arrows), using ODR-3, OSM-9, OCR2 and the inhibitor GRK-2. We propose that, upon prolonged exposure to attractive NaCl concentrations, an ASE-derived signal sensitises the ASH, ADL, ASI and ADF neurons, resulting in avoidance of normally attractive NaCl concentrations. We have shown that the ADF neurons use ODR-3, and the ASI neurons, a second pathway in the ASH neurons and probably the ADL neurons use GPC-1. Integration of these signals ultimately leads to the behavioural response of the animal.
