Figure 5.
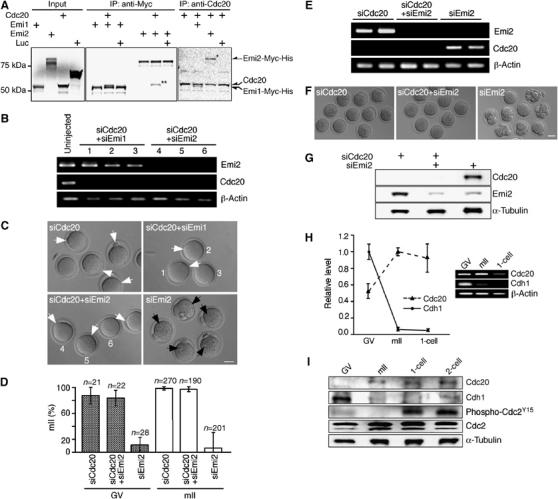
Cytostatic arrest by Emi2 requires Cdc20. (A) Co-immunoprecipitation of full-length Cdc20 and Emi1-Myc-His or Emi2-Myc-His fusions produced in vitro. Radiolabeled proteins were immunoprecipitated with anti-Cdc20 or anti-Myc antibodies and subjected to SDS–PAGE prior to autoradiography. Co-precipitated proteins corresponding to Emi2-Myc-His and Cdc20 are respectively marked with one or two asterisks. (B) RT–PCR for Emi2, Cdc20 and β-actin transcripts 29 h after injection of GV oocytes with [siEmi2#1+siCdc20#1], [siEmi1#2+siCdc20#1], siCdc20#1 or without injection. (C) Hoffman modulation micrographs of oocytes 29 h after GV oocyte injection as per (B). Numbers in (B) and (C) refer to the same cells; key to labeling is as per Figure 3. Bar=50 μm. (D) Average percentages arrested at mII, respectively, 29 and 23 h after injection of GV (stipled) or mII (open) oocytes with siRNAs as indicated. (E) RT–PCR for Emi2, Cdc20 and β-actin transcripts 23 h after injection of mII oocytes with siEmi2#1, [siEmi2#1+siCdc20#1], or siCdc20#1. (F) Phase contrast micrographs 23 h after oocyte injection as per (E). Bar=50 μm. (G) Immunoblotting of mII oocytes 23 h after injection with siRNAs (+) against Cdc20 and/or Emi2 mRNAs. Developmental profiles of (H) Cdh1 and Cdc20 mRNA levels shown by (q)PCR (left) and gel electrophoresis, and (I) Cdh1, Cdc20, Cdc2 and phospho-Cdc2Y15 and α-tubulin (loading control) proteins in a single Western blot.
