Figure 3.
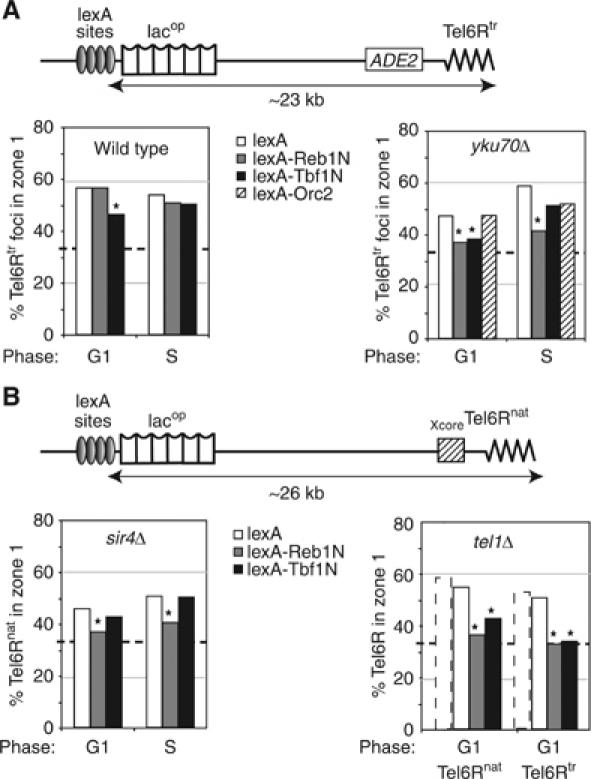
Role of Reb1 and Tbf1 in telomere anchoring. (A) The indicated LexA fusions were targeted to four lexA-binding sites located ∼23 kb from the end of truncated Tel6R. Reb1 and Tbf1 domains encompass the transactivation domain (aa 1–405). Orc2 is a full-length fusion. Position of Tel6Rtr was monitored in cells expressing lexA alone (white boxes), lexA-Reb1N (grey boxes), lexA-Tbf1N (black boxes) or a lexA-Orc2 fusion (hatched boxes) in G1 cells of isogenic wild-type (GA-1917) or yku70Δ (GA-1918) strains. (B) As in (A) except that where indicated strains bear the native Tel6R (Tel6Rnat; GA-1459) with either sir4Δ (GA-1867) or tel1Δ (GA-3453). Tel6Rtr is also monitored in a tel1Δ train (GA-3052). Stipled bars indicate values for the same telomeres with lexA in a wild-type background. Symbols are as in Figure 2, and S phase and P-values are in Supplementary Table 1.
