Figure 1.
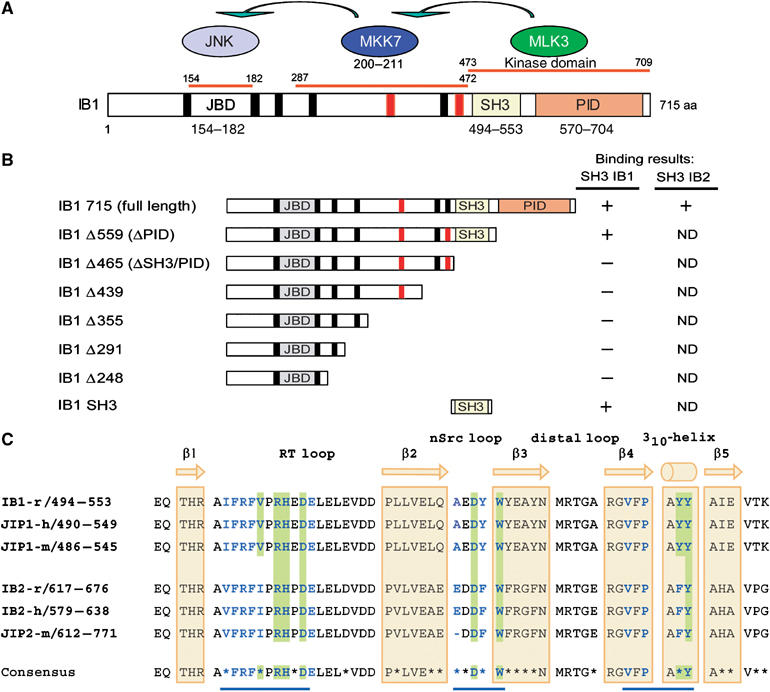
Protein interaction domains of IB1. (A) IB1 is characterized by a JBD (gray box, residues 154–182), SH3 (yellow box, residues 494–553) and a PID (orange box, residues 570–704). Residues are numbered according to the full-length rat IB1 sequence (GenBank, AF108959). The seven PxxP motifs are shown in black and red. Motifs marked in red are conserved in rat, human and mouse IB1 and IB2. MKK7 and MLK3, two of the known partners of IB1, bind to regions 287–472 and 473–709 of IB1, respectively. (B) Schematic representations of full-length and C-terminal deletion mutants of IB1. Numbering corresponds to the last amino-acid expressed in the various constructs. Binding results described in Figure 2 are summarized for all constructs. ND: not determined. (C) Sequence alignment of rat, mouse and human IB1/JIP1 and IB2/JIP2 SH3 domains. The sequence of rat IB1 (GenBank, AF108959), human JIP1 (Ensembl, ENSP00000241014), mouse JIP1 (Ensembl, ENSMUSP00000050773), rat IB2 (Ensembl, ENSRNOP00000050155), human IB2 (GenBank, AF218778) and mouse JIP2 (Ensembl, ENSMUSP00000023291) are included. The IB1 SH3 region is identical in all three species. Residues that participate to IB1 dimerization as well as those expected to do so in IB2 are shown in bold blue. Residues at the dimer interface involved in inter-protomer salt bridges or hydrogen bonds are shaded in green. Nonconserved amino acids between IB1 and IB2 are indicated with a star in the consensus sequence. The positions of the β strands 1–5 and the 310-helix are indicated in yellow.
