Figure 3.
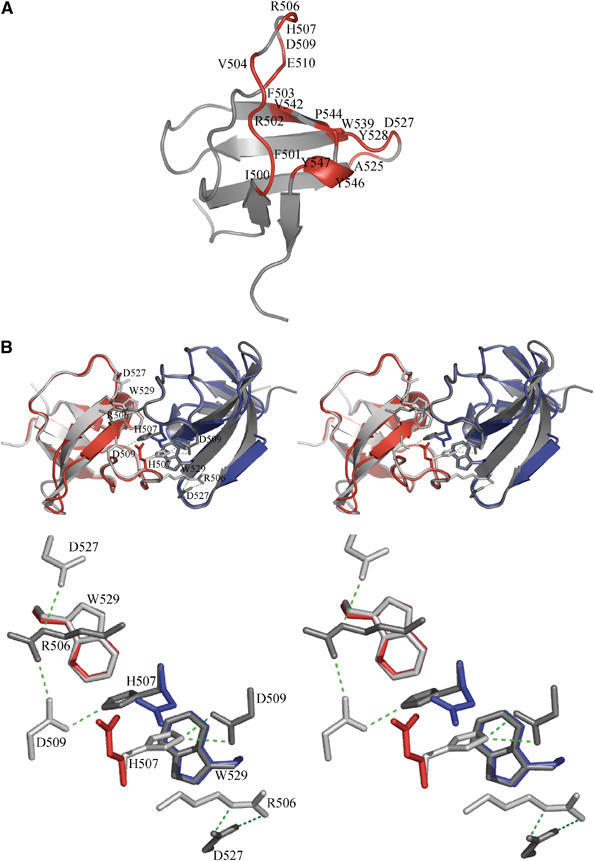
Structure of the IB1 SH3 domain. (A) Cartoon representation of the IB1 SH3 domain (in gray). The structure is composed of five β-strands arranged into two antiparallel sheets. The first sheet is formed by strands 1 and 5 and the second sheet by the strands 2, 3 and 4. The IB1 SH3 domain forms a dimer. Residues contacting the other protomer (Table II) are colored in red and labeled. (B) Cartoon representations of the experimentally determined IB1 SH3 homodimer (gray) and of the artificial C-terminal Grb2 SH3 dimer (in red and blue) generated by superposition onto the IB1 SH3 backbone (shown in stereo). The two IB1 SH3 protomers in the dimer are in a cis arrangement and it is likely that the two PID domains are in close proximity to each other. The superimposed Grb2 dimer illustrates that in this structure two opposing glutamate residues (red and blue) are incompatible with IB1-like homodimerization (see enlargement).
