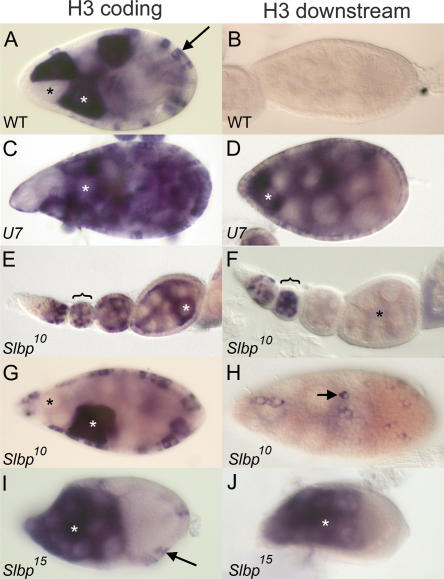
FIGURE 7.
U7 and SLBP are required for histone pre-mRNA processing during oogenesis. (A) w1118 control egg chamber hybridized with a histone H3 coding probe. In this and subsequent panels, white and black asterisks indicate individual nurse cells with and without H3 mRNA, respectively, and arrows indicate follicle cells. (B) w1118 control egg chamber hybridized with an H3-ds probe. Note the lack of staining because H3-ds only detects misprocessed, poly A+ histone H3 mRNA. (C,D) U714 mutant egg chambers hybridized with H3 coding and H3-ds probes, respectively. (E,F) Early stage Slbp10 mutant egg chambers, each from an individual ovariole, hybridized with the H3 coding and H3-ds probes, respectively. The brackets indicate a stage 2 or 3 egg chamber with staining in the nurse cells undergoing endocycles. Note the absence of H3-ds probe in the older egg chambers (asterisk in F). (G) Slbp10 mutant egg chamber stained with the H3 probe indicating production of H3 mRNA in both nurse and follicle cells. (H) Slbp10 mutant egg chamber hybridized with an H3-ds probe, with focus on the follicle cells. The arrow indicates a follicle cell expressing misprocessed, poly A+ histone mRNA. (I,J) Mosaic egg chambers containing Slbp15 mutant germ cells hybridized with a histone H3 coding probe (I) or an H3-ds probe (J). Because this is a mosaic egg chamber, the follicle cells are phenotypically wild-type and do not stain with the H3-ds probe because they express only wild-type H3 mRNA (arrow in I). All egg chambers except E and F stage 9. Anterior at left and posterior at right in all panels.