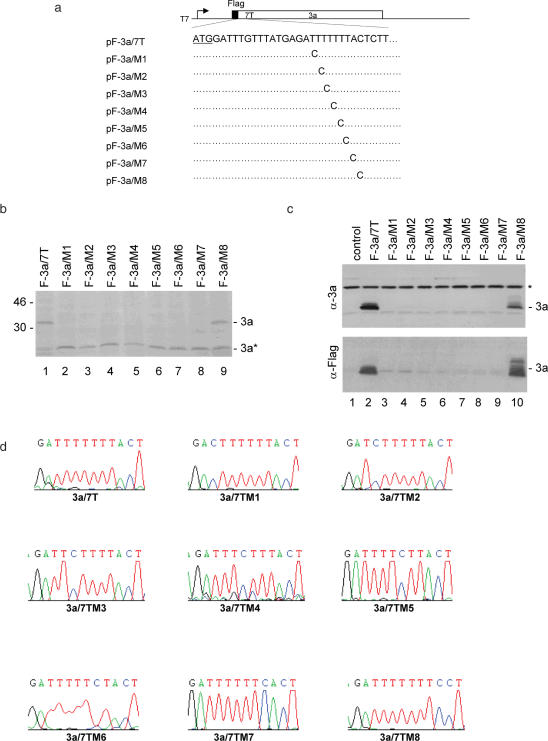
Figure 2.
Mutational analysis of the slippery sequence in pF-3a/7T. (a) Diagram of pF-3a/7T and the eight mutants (pF-3a/M1-M8). The initiator ATG codon for 3a is underlined. Also shown are the point mutations introduced into the seven T stretch in each mutant constructs. (b) Expression of pF-3a/7T (lane 1) and mutant constructs (lanes 2–9) in vitro in reticulocyte lysates. Polypeptides were labeled with [35S]methionine, separated on SDS–12% polyacrylamide gel and detected by autoradiography. Bands corresponding to the full-length 3a and a minor species 3a* representing an internal initiation product are indicated. Numbers on the left indicate molecular masses in kilodaltons. (c) Expression of pF-3a/7T and mutant constructs in Cos-7 cells. Cells were infected with the recombinant vaccinia/T7 virus, and transfected with an empty control plasmid (lane 1), pF-3a/7T (lane 2) and the eight mutant constructs (lanes 3–10), respectively. At 18 h posttransfection, cells were harvested and lysates prepared. Polypeptides were separated on SDS–12% polyacrylamide and analyzed by western blot with either anti-3a polyclonal (upper panel) or anti-Flag monoclonal antibodies (lower panel). A background band detected by this antiserum is indicated by asterisk. (d) No deletion of nucleotides or revision of mutations in the seven T regions during transcription of wild type and mutant constructs. Cos-7 cells transfected with pF-3a/7T and the eight mutant constructs, respectively, were lysed by Trizol reagent at 24 h post transfection. Total RNA was extracted from cells expressing and 1 µg of RNA was used for RT–PCR. The RT–PCR products were sequenced by automated nucleotide sequencing. The seven T regions of the RT–PCR products are shown.