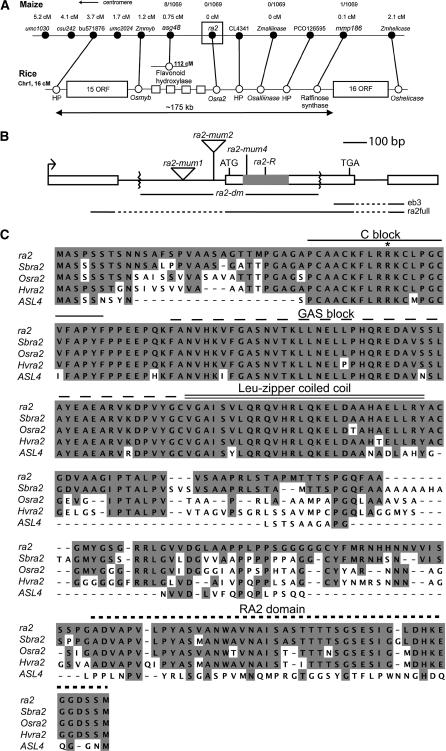
Figure 3.
Cloning and Characterization of ra2.
(A) The genetic map of a portion of maize chromosome 3 (top) is compared with the syntenous physical region of rice chromosome 1 (bottom). Black circles are maize markers/genes. White circles are rice genes and ORFs. The 175-kb segment indicated for the rice physical map corresponds to rice clone AP003339. The rice homolog to maize RFLP marker asg48 is located in an unlinked location of rice chromosome 1, and it is the only nonsyntenic gene of the region shown here between maize and rice. There are four ORFs (white squares) in a 17-kb region between the Osmyb and Osra2 genes for which there are no significantly similar maize sequences. The number and order of rice genes follow their annotation in GenBank but are not drawn to proportion. HP, hypothetical protein.
(B) Structure of ra2 with the LOB domain in gray; diagram begins and ends at transcription initiation and polyadenylation site, respectively. The alleles of ra2 are shown with the ra2-dm deletion indicated by the zigzag marks in intron 1 and exon 2. eb3, the fragment used as a probe for DNA and RNA gel blot hybridizations; ra2full, the probe used for in situ hybridizations.
(C) Alignment of the deduced full-length amino acid sequence of ra2 from maize, sorghum (Sbra2), rice (Osra2), barley (Hvra2), and ASL4 of Arabidopsis. The LOB domain is located near the N terminus and consists of a C-rich domain, a GAS block, and a Leu-zipper domain. Grass ra2 orthologs share a conserved C terminus domain of unknown function. The asterisk indicates the mutation (Arg to His) in the ra2-mum4 allele.