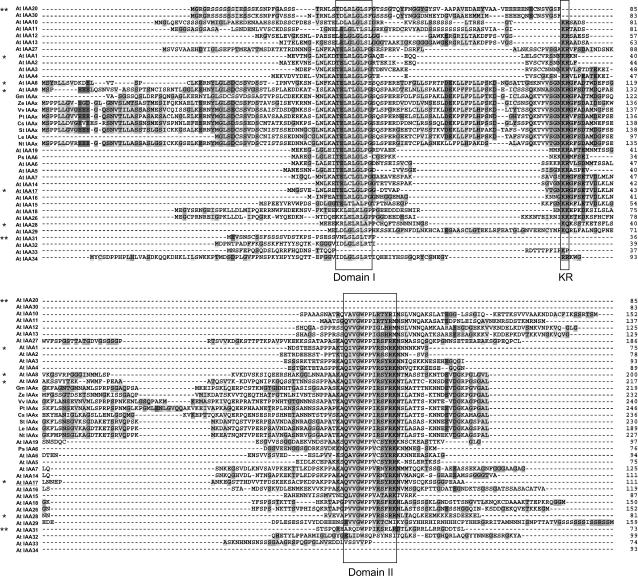
Figure 1.
Alignment of Aux/IAA Family Members from the N Terminus to the Beginning of Domain III.
All Aux/IAA family members from Arabidopsis (Liscum and Reed, 2002), one rapidly degraded family member from pea, and several Aux/IAA proteins from other plant species were aligned using ClustalX (version 1.8) followed by manual editing using MacClade 4.05 OS X. All amino acids from the N terminus to the amino acid just before the beginning of domain III were included. Single asterisks mark canonical family members and double asterisks mark noncanonical family members analyzed in this study. Two groups of conserved amino acids within IAA17 (underlined name), a representative canonical family member, were changed for a series of experiments (see Figures 2 and 3). Conserved domains (Abel et al., 1995; Ramos et al., 2001; Tiwari et al., 2004) are boxed and vary slightly from domain I and domain II predictions from Abel et al. (1995) and Tiwari et al. (2004). Different shades of gray highlight specific subsets of amino acids according to default parameters in ClustalX. Sequences were obtained from The Arabidopsis Information Resource (TAIR) (Arabidopsis IAAs) or were identified using BLASTP at the National Center for Biotechnology Information (other species). At, Arabidopsis thaliana; Gm, Glycine max; Ze, Zinnia elegans; Vv, Vitis vinifera; Pt, Populus tremula × Populus tremuloides; St, Solanum tuberosum; Le, Lycopersicon esculentum; Cs, Cucumis sativus; Nt, Nicotiana tabacum; Ps, Pisum sativum.