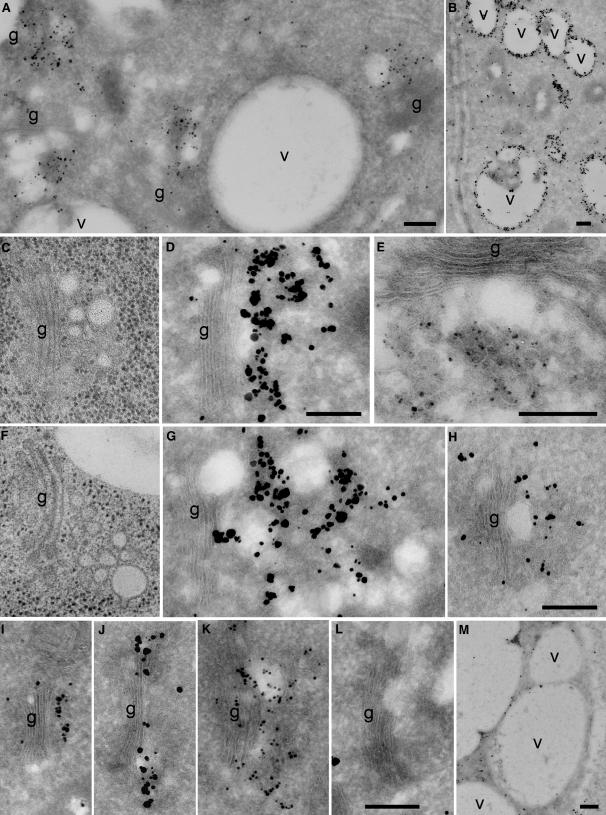
Figure 2.
Immunogold Localization of VHA-a1–GFP and TGN Morphology.
Immunogold labeling of ultrathin cryosections was performed with anti-GFP antibodies ([A], [D], [E], [G], and [I] to [L]) or anti–VHA-E antibodies ([B], [H], and [M]) and silver-enhanced Nanogold IgG. In (L), silver-enhanced Qdot525 IgG was used as a marker.
(A) Overview of an immunogold-labeled cryosection of a root tip cortex cell expressing VHA-a1–GFP. Gold markers accumulate in the vicinity of Golgi stacks (g).
(B) The anti–VHA-E antibody strongly labels vacuolar membranes (v) and, to a lesser extent, the TGN region (see [H]).
(C) and (F) Electron micrographs of Golgi stacks and their associated TGNs in high-pressure frozen and freeze-substituted root tip cortex cells, shown at the same magnification as (D), (G), and (H).
(D), (E), and (G) Golgi stacks and their associated TGNs after immunogold labeling of VHA-a1–GFP in root cortex cells.
(H) Labeling of wild-type cells using anti–VHA-E antibodies results in gold labeling in the vicinity of Golgi stacks and on vacuolar membranes (see [B]).
(I) The a1a2-GFP chimeric protein can be detected on the TGN.
(J) and (K) N-ST-GFP is located at the trans-most Golgi cisternae (J) and often also in the TGN (K). Labeling of N-ST-GFP with the silver-enhanced Quantum dot marker (Qdot525) (J) resulted in a labeling pattern and label density similar to those of silver-enhanced Nanogold markers.
(L) Control labeling on wild-type root cryosections using anti-GFP antibodies and silver-enhanced Nanogold was negligible.
(M) Control labeling with anti–VHA-E antibodies on cryosections of a VHA-E1–deficient embryo (Strompen et al., 2005). There are only a few gold particles on vacuolar membranes.
Bars = 0.25 μm.