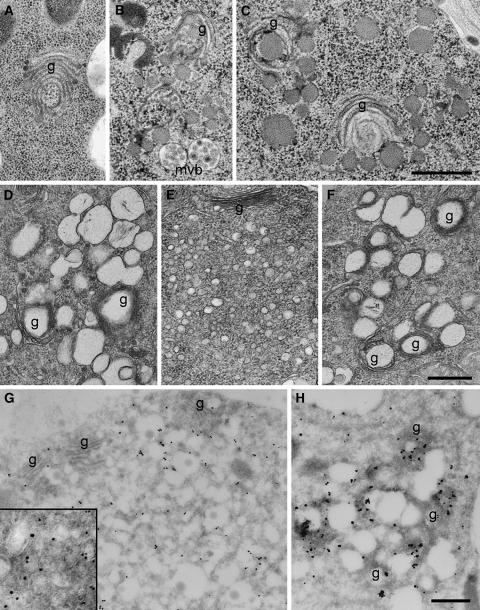
Figure 5.
ConcA Induces Changes of TGN and Golgi Stack Morphology and Interferes with BFA Action.
(A) to (C) Electron micrographs of high-pressure frozen and freeze-substituted root tip cortex cells showing changes in Golgi and TGN morphology after ConcA treatment, such as the characteristic bending and swelling of the ends of cisternae (A) and the fragmentation of Golgi stacks and the accumulation of large vesicles ([B] and [C]). g, Golgi stack; mvb, multivesicular bodies.
(D) to (F) Electron micrographs of chemically fixed root tip cortex cells showing vesicle agglomerations induced by ConcA (D), BFA (E), and ConcA followed by BFA (F). The content of ConcA-induced vesicles is lost after chemical fixation and dehydration at ambient temperature (cf. [C]).
(G) and (H) Immunogold labeling of VHA-a1–GFP on cryosections of root tip cortex cells using anti-GFP antibodies and silver-enhanced Nanogold after ConcA treatment (G) and BFA treatment (H). BFA and ConcA compartments are labeled. The inset in (H) shows a 2.5× enlarged detail of a thicker cryosection with gold-labeled vesicles of different sizes.
Bars = 0.5 μm.