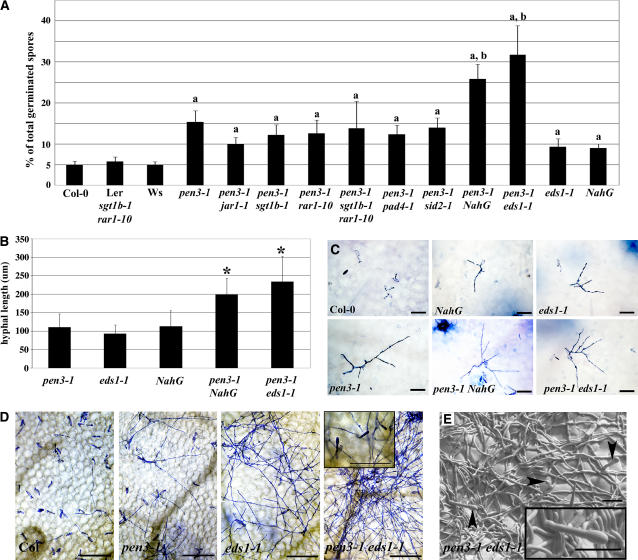
Figure 5.
Combined Mutations in PEN3 and EDS1or Introduction of the NahG Transgene Compromise Nonhost Resistance to B. g. hordei and E. pisi.
(A) Mean of the frequency of B. g. hordei penetration on Arabidopsis, expressed as a percentage of total germinated spores. Wassilewskija (Ws) is the wild-type control for eds1-1; Ler sgt1b-1 rar1-10 is the control for double mutants with sgt1b-1 and rar1-10; and Col-0 is the wild-type control for npr1-1, sid2-1, pad4-1, jar1-1, and NahG. Eight leaves per genotype were stained with aniline blue at 2 DAI, and the occurrence of callose-encased haustoria was monitored as a measure of penetration efficiency. a Significantly different from the wild type; b significantly different from pen3 using Student's t test (P < 0.001).
(B) Average hyphal length of B. g. hordei colonies growing on different mutants. Leaves were stained with trypan blue at 10 DAI, and hyphal lengths per colony were measured from photographs using ImageJ software. A minimum of 10 colonies were measured for hyphal length. This experiment was repeated twice. * Significantly different from the corresponding value for pen3 using Student's t test (P < 0.001).
(C) Examples of B. g. hordei colonies growing on different lines. Infected leaves were stained with trypan blue at 10 DAI. Bars = 30 μm.
(D) E. pisi growth on Col-0 leaves and the indicated mutant genotypes at 7 DAI. Light microscopic images were taken after visualization of fungal structures using Coomassie Brilliant Blue. Bars = 200 μm. The inset shows a close-up view of E. pisi conidiophores on the pen3-1 eds1-1double mutant. Bar = 50 μm.
(E) Cryogenic scanning electron micrograph of E. pisi growth on pen3-1 eds1-1 at 7 DAI. The inset shows an E. pisi conidiophore. Bars = 50 μm.