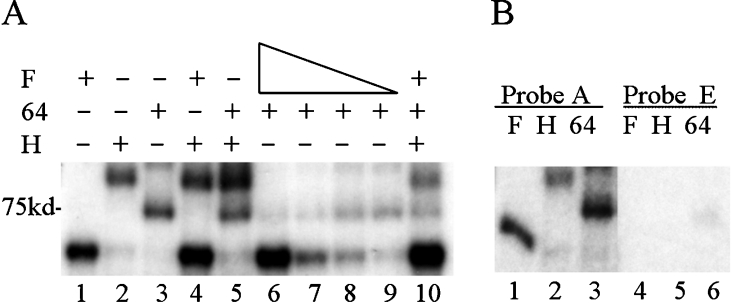
Figure 2. hnRNP F inhibits CstF-64 binding.
Purified hnRNP proteins and/or the RNA-binding domain of CstF-64 were incubated with 32P-labelled RNA under UV-cross-linking conditions (see the Experimental section) and subjected to UV-irradiation on ice. Following RNase digestion, proteins were separated by SDS/10% PAGE. Dried gels were exposed to film. In the indicated lanes, 50 nM GST-tagged hnRNP H2 or 260 nM GST–CstF-64 RBD were added. (A) Lane 1, 40 nM His-hnRNP F; lane 2, GST-hnRNP H2; lane 3, GST–CstF-64 RBD; lane 4, 40 nM His–hnRNP F plus GST–hnRNP H2; lane 5, GST–hnRNP H2 plus GST–CstF-64 RBD; lane 6, 40 nM His–hnRNP F plus GST–CstF-64 RBD; lane 7, 20 nM His–hnRNP F plus GST–CstF-64 RBD; lane 8, 10 nM His–hnRNP F plus GST–CstF-64 RBD; lane 9, 5 nM His–hnRNP F plus GST–CstF-64 RBD; lane 10, 40 nM His–hnRNP F, GST–CstF-64 RBD and GST–hnRNP H2. (B) SVL or SVL-GEM, probes A or E incubated with purified proteins; lanes 1 and 4, 40 nM His–hnRNP F; lanes 2 and 5, 50 nM GST–hnRNP H2; lanes 3 and 6, 260 nM GST–CstF-64 RBD. The position of the 75 kDa protein is indicated. F, hnRNP F; H, hnRNP H; 64, CstF-64.