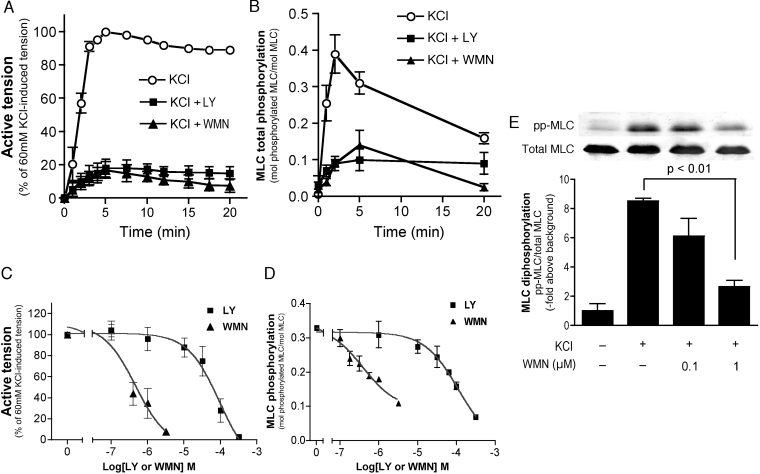
Figure 1. Inhibition of membrane depolarization-induced contraction and MLC phosphorylation by PI3K inhibitors.
Time-dependent changes of KCl (60 mM)-induced contraction (A) and total MLC phosphorylation (B) in the presence and absence of WMN (1 μM) or LY (100 μM). Dose-dependent inhibition of KCl (60 mM)-induced contraction (C) and total MLC phosphorylation (D) at 5 min by PI3K inhibitors. (E) Inhibition of KCl-induced increase in the content of pp-MLC (di-phosphorylated form of MLC) by a high, but not a low, concentration of WMN. VSM was pretreated with the indicated concentrations of WMN and stimulated with 60 mM KCl for 5 min. The content of pp-MLC was analysed by using anti-pp-MLC-specific antibody. A portion of extracts was analysed for the content of total MLC by Western blot analysis using anti-MLC antibody (MY21). In all panels, PI3K inhibitors were added to VSM 30 min before KCl stimulation.