Abstract
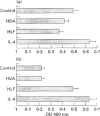
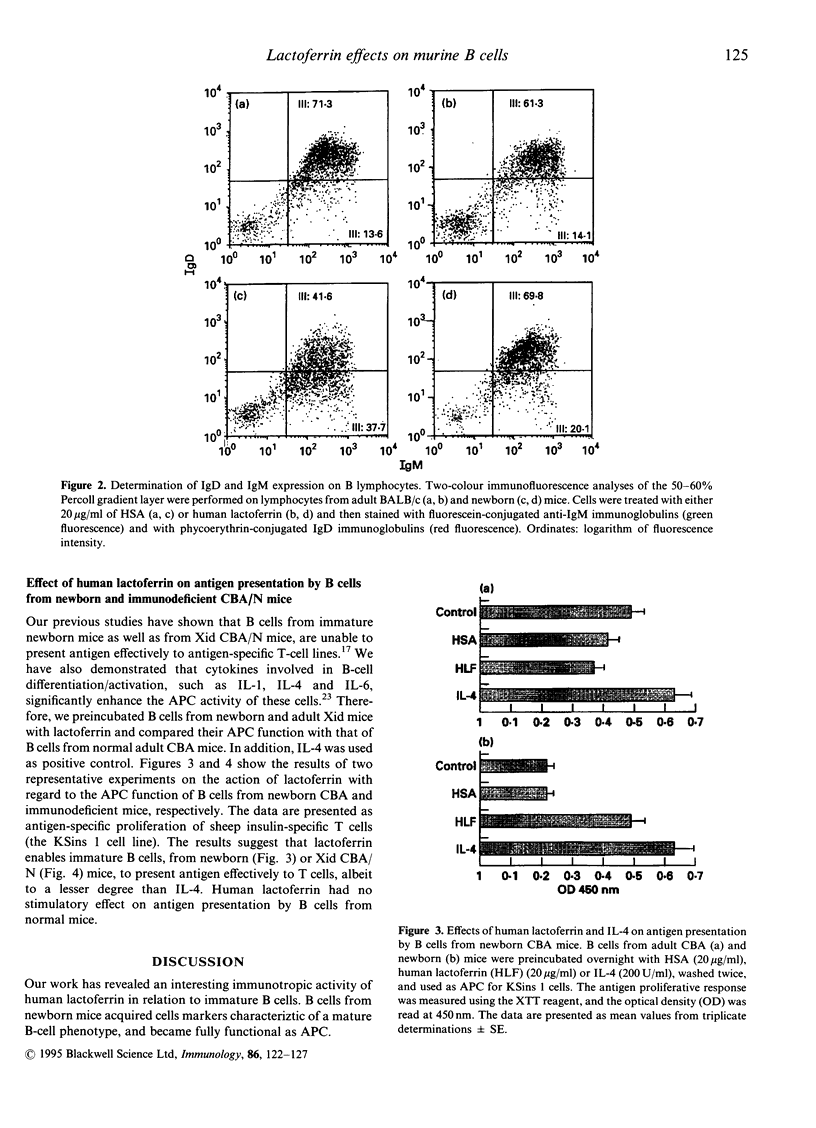
The immunotropic activities of human lactoferrin were studied with respect to phenotypic and functional changes in murine splenic B cells. Phenotypic changes were induced by human lactoferrin in splenic B-cell fractions separated by buoyant density. B cells from 7-8-day-old BALB/c mice isolated from a 50/60% Percoll gradient, gained characteristic features of more mature B cells manifested by an increase of surface IgD and complement receptor expression. Incubation of the analogous B-cell fraction from adult mice with human lactoferrin resulted in minor changes in relation to IgM and IgD expression. Besides induction of phenotypic changes on immature B cells, human lactoferrin enabled B cells from normal newborn and adult immunodeficient CBA/N mice to present antigen to an antigen-specific T-helper type 2 (Th2) cell line. We conclude that human lactoferrin acts as a maturation factor for B cells with regard to their phenotype and function.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brines R. D., Klaus G. G. Inhibition of lipopolysaccharide-induced activation of immature B cells by anti-mu and anti-delta antibodies and its modulation by interleukin-4. Int Immunol. 1992 Jul;4(7):765–771. doi: 10.1093/intimm/4.7.765. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crouch S. P., Slater K. J., Fletcher J. Regulation of cytokine release from mononuclear cells by the iron-binding protein lactoferrin. Blood. 1992 Jul 1;80(1):235–240. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gelfand M. C., Elfenbein G. J., Frank M. M., Paul W. E. Ontogeny of B lymphocytes. II. Relative rates of appearance of lymphocytes bearing surface immunoglobulin and complement receptors. J Exp Med. 1974 May 1;139(5):1125–1141. doi: 10.1084/jem.139.5.1125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hashizume S., Kuroda K., Murakami H. Identification of lactoferrin as an essential growth factor for human lymphocytic cell lines in serum-free medium. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Dec 19;763(4):377–382. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(83)90099-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kearney J. F., Cooper M. D., Klein J., Abney E. R., Parkhouse R. M., Lawton A. R. Ontogeny of Ia and IgD on IgM-bearing B lymphocytes in mice. J Exp Med. 1977 Jul 1;146(1):297–301. doi: 10.1084/jem.146.1.297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimoto M., Fathman C. G. Antigen-reactive T cell clones. I. Transcomplementing hybrid I-A-region gene products function effectively in antigen presentation. J Exp Med. 1980 Oct 1;152(4):759–770. doi: 10.1084/jem.152.4.759. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lay W. H., Nussenzweig V. Receptors for complement of leukocytes. J Exp Med. 1968 Nov 1;128(5):991–1009. doi: 10.1084/jem.128.5.991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leveugle B., Mazurier J., Legrand D., Mazurier C., Montreuil J., Spik G. Lactotransferrin binding to its platelet receptor inhibits platelet aggregation. Eur J Biochem. 1993 May 1;213(3):1205–1211. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1993.tb17871.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MONTREUIL J., TONNELAT J., MULLET S. [Preparation and properties of lactosiderophilin (lactotransferrin) of human milk]. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1960 Dec 18;45:413–421. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(60)91478-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Machnicki M., Zimecki M., Zagulski T. Lactoferrin regulates the release of tumour necrosis factor alpha and interleukin 6 in vivo. Int J Exp Pathol. 1993 Oct;74(5):433–439. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masson P. L., Heremans J. F., Schonne E. Lactoferrin, an iron-binding protein in neutrophilic leukocytes. J Exp Med. 1969 Sep 1;130(3):643–658. doi: 10.1084/jem.130.3.643. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazurier J., Legrand D., Hu W. L., Montreuil J., Spik G. Expression of human lactotransferrin receptors in phytohemagglutinin-stimulated human peripheral blood lymphocytes. Isolation of the receptors by antiligand-affinity chromatography. Eur J Biochem. 1989 Feb 1;179(2):481–487. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1989.tb14578.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazurier J., Spik G. Comparative study of the iron-binding properties of human transferrins. I. Complete and sequential iron saturation and desaturation of the lactotransferrin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 May 7;629(2):399–408. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(80)90112-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyazawa K., Mantel C., Lu L., Morrison D. C., Broxmeyer H. E. Lactoferrin-lipopolysaccharide interactions. Effect on lactoferrin binding to monocyte/macrophage-differentiated HL-60 cells. J Immunol. 1991 Jan 15;146(2):723–729. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris J. F., Hoyer J. T., Pierce S. K. Antigen presentation for T cell interleukin-2 secretion is a late acquisition of neonatal B cells. Eur J Immunol. 1992 Nov;22(11):2923–2928. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830221125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Narendran A., Ramsden D., Cumano A., Tanaka T., Wu G. E., Paige C. J. B cell developmental defects in X-linked immunodeficiency. Int Immunol. 1993 Feb;5(2):139–144. doi: 10.1093/intimm/5.2.139. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rochard E., Legrand D., Lecocq M., Hamelin R., Crepin M., Montreuil J., Spik G. Characterization of lactotransferrin receptor in epithelial cell lines from non-malignant human breast, benign mastopathies and breast carcinomas. Anticancer Res. 1992 Nov-Dec;12(6B):2047–2051. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roehm N. W., Rodgers G. H., Hatfield S. M., Glasebrook A. L. An improved colorimetric assay for cell proliferation and viability utilizing the tetrazolium salt XTT. J Immunol Methods. 1991 Sep 13;142(2):257–265. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(91)90114-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scher I., Berning A. K., Kessler S., Finkelman F. D. Development of B lymphocytes in the mouse; studies of the frequency and distribution of surface IgM and IgD in normal and immune-defective CBA/N F1 mice. J Immunol. 1980 Oct;125(4):1686–1693. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scher I. The CBA/N mouse strain: an experimental model illustrating the influence of the X-chromosome on immunity. Adv Immunol. 1982;33:1–71. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60834-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schittek B., Rajewsky K. Natural occurrence and origin of somatically mutated memory B cells in mice. J Exp Med. 1992 Aug 1;176(2):427–438. doi: 10.1084/jem.176.2.427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schryvers A. B., Morris L. J. Identification and characterization of the human lactoferrin-binding protein from Neisseria meningitidis. Infect Immun. 1988 May;56(5):1144–1149. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.5.1144-1149.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. R., Yaffe L. J., Chused T. M., Raveche E. S., Klinman D. M., Steinberg A. D. Analysis of B-cell subpopulations. I. Relationships among splenic xid, Ly 1+, and Lyb 5+ B cells. Cell Immunol. 1985 Apr 15;92(1):190–196. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(85)90077-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spik G., Strecker G., Fournet B., Bouquelet S., Montreuil J., Dorland L., van Halbeek H., Vliegenthart J. F. Primary structure of the glycans from human lactotransferrin. Eur J Biochem. 1982 Jan;121(2):413–419. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb05803.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vitetta E. S., Melcher U., McWilliams M., Lamm M. E., Phillips-Quagliata J. M., Uhr J. W. Cell surface immunoglobulin. XI. The appearance of an IgD-like molecule on murine lymphoid cells during ontogeny. J Exp Med. 1975 Jan 1;141(1):206–215. doi: 10.1084/jem.141.1.206. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zagulski T., Lipiński P., Zagulska A., Broniek S., Jarzabek Z. Lactoferrin can protect mice against a lethal dose of Escherichia coli in experimental infection in vivo. Br J Exp Pathol. 1989 Dec;70(6):697–704. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimecki M., Kapp J. A. Presentation of antigen by B cell subsets. III. Effects of interleukins on antigen presenting function and phenotype of immature B cells. Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz) 1994;42(5-6):355–359. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimecki M., Kapp J. A. Presentation of antigen by B cell subsets. IV. Defective T-B cell signalling causes inability to present antigen by B cells from immunodeficient mice. Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz) 1994;42(5-6):361–367. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimecki M., Mazurier J., Machnicki M., Wieczorek Z., Montreuil J., Spik G. Immunostimulatory activity of lactotransferrin and maturation of CD4- CD8- murine thymocytes. Immunol Lett. 1991 Sep;30(1):119–123. doi: 10.1016/0165-2478(91)90099-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimecki M., Whiteley P. J., Pierce C. W., Kapp J. A. Presentation of antigen by B cells subsets. I. Lyb-5+ and Lyb-5- B cells differ in ability to stimulate antigen specific T cells. Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz) 1994;42(2):115–123. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]