Abstract
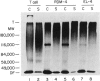
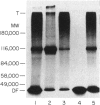
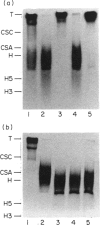
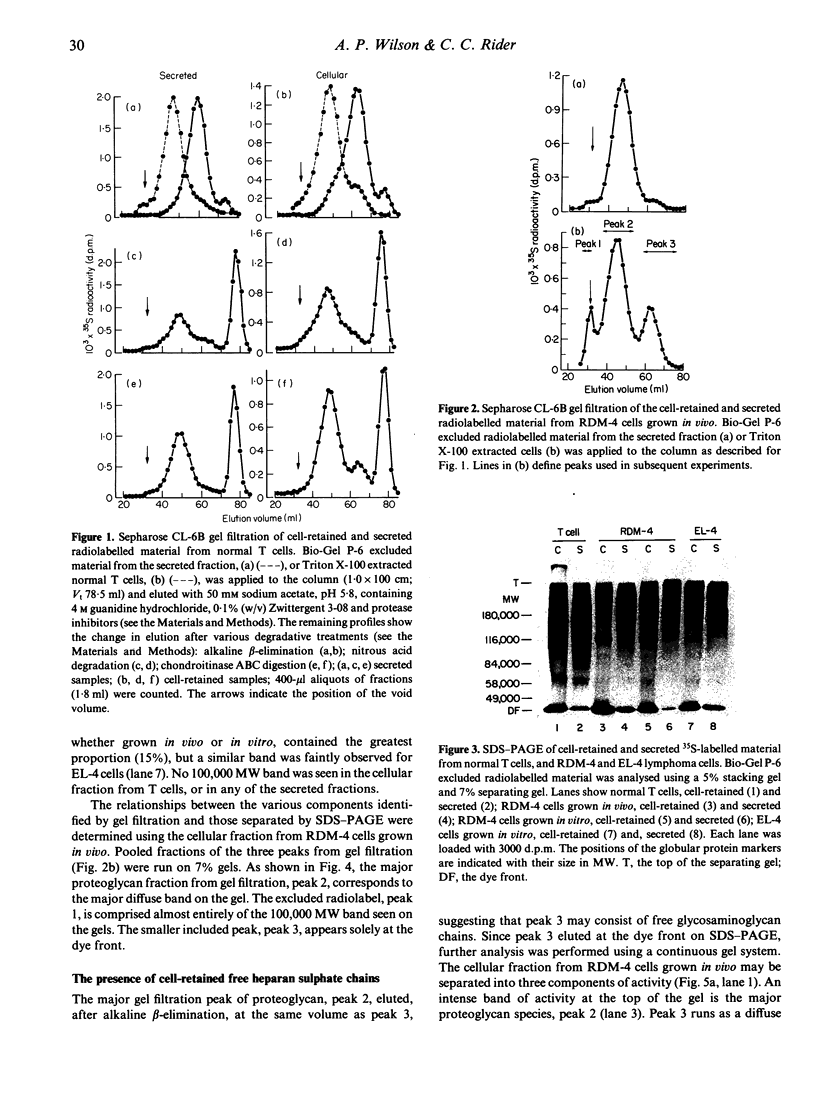
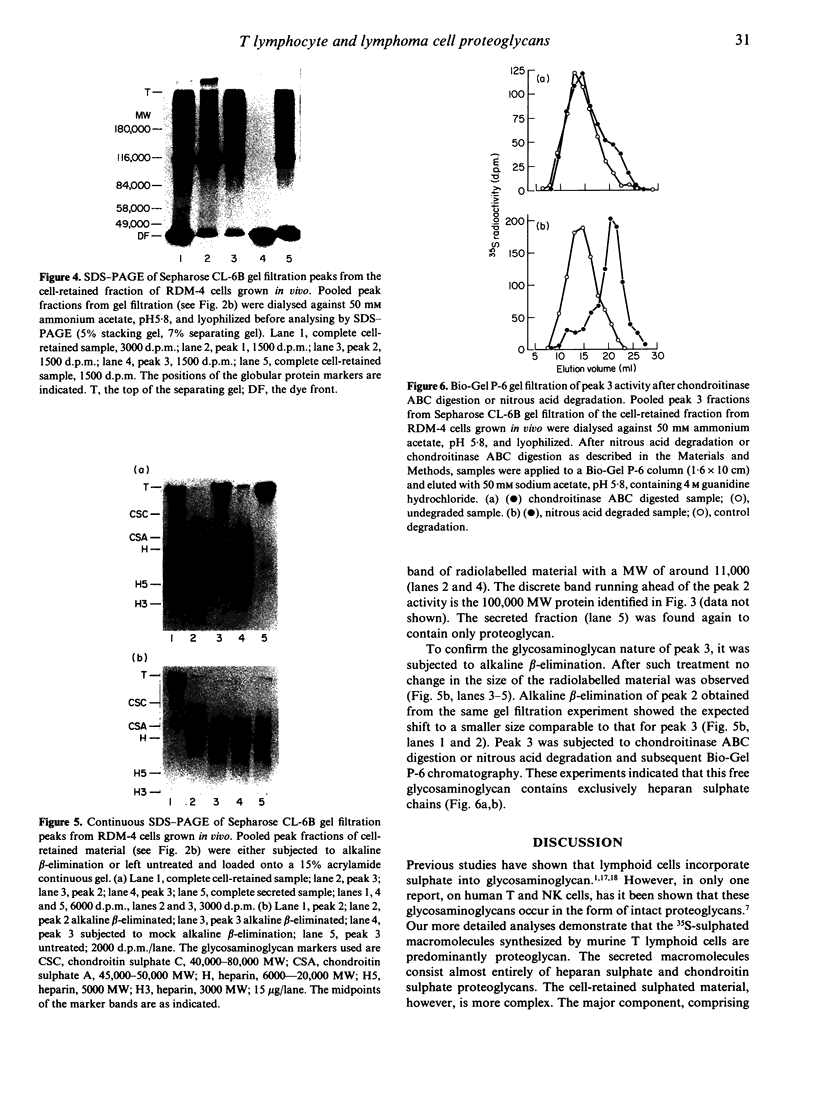
Normal murine splenic T lymphocytes and T-lymphoma cells were incubated with [35S]sulphate in low-sulphate medium for 4 hr. Gel filtration and SDS-PAGE revealed that the radiolabelled macromolecules secreted by these cells were almost exclusively chondroitin sulphate and heparan sulphate proteoglycans of relatively low molecular weight (MW), 100,000-200,000. Triton X-100 extracts of the cells contained similar proteoglycans. Under the conditions employed the incorporation of radiolabel by cells grown in vivo was equally distributed between cell-retained and secreted fractions, whereas cells grown in vitro retained some 75% of incorporated label. In general heparan sulphate predominated over chondroitin sulphate in both secreted and cell-retained fractions. Cell extracts also contained a minor proportion of free glycosaminoglycan, which is almost exclusively heparan sulphate. These chains, like those incorporated into the proteoglycan, were around 12,000 MW. The T-lymphoma cells RDM-4, whether grown in vitro or in vivo, also incorporated a substantial proportion of [35S]sulphate into a single, cell-retained protein, 100,000 MW. No such radiolabelled protein was detectable in T cells.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bartold P. M., Haynes D. R., Vernon-Roberts B. Effect of mitogen and lymphokine stimulation on proteoglycan synthesis by lymphocytes. J Cell Physiol. 1989 Jul;140(1):82–90. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041400111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradbury M. G., Parish C. R. Receptors on lymphocytes for endogenous splenic glycosaminoglycans. Immunology. 1989 Apr;66(4):546–553. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlson D. M. Structures and immunochemical properties of oligosaccharides isolated from pig submaxillary mucins. J Biol Chem. 1968 Feb 10;243(3):616–626. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christmas S. E., Steward W. P., Lyon M., Gallagher J. T., Moore M. Chondroitin sulphate proteoglycan production by NK cells and T cells: effects of xylosides on proliferation and cytotoxic function. Immunology. 1988 Feb;63(2):225–231. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen S. B., Coligan J. E., Freed J. H. Isolation and biochemical characterization of the H-2Kk and H-2Dk antigens from the RDM-4 lymphoma. Mol Immunol. 1984 Jun;21(6):449–459. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(84)90060-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hampson I. N., Gallagher J. T. Separation of radiolabelled glycosaminoglycan oligosaccharides by polyacrylamide-gel electrophoresis. Biochem J. 1984 Aug 1;221(3):697–705. doi: 10.1042/bj2210697. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hart G. W. Biosynthesis of glycosaminoglycans by thymic lymphocytes. Effects of mitogenic activation. Biochemistry. 1982 Nov 23;21(24):6088–6096. doi: 10.1021/bi00267a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jalkanen S., Jalkanen M., Bargatze R., Tammi M., Butcher E. C. Biochemical properties of glycoproteins involved in lymphocyte recognition of high endothelial venules in man. J Immunol. 1988 Sep 1;141(5):1615–1623. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lederman S., Gulick R., Chess L. Dextran sulfate and heparin interact with CD4 molecules to inhibit the binding of coat protein (gp120) of HIV. J Immunol. 1989 Aug 15;143(4):1149–1154. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levitt D., Ho P. L. Induction of chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan synthesis and secretion in lymphocytes and monocytes. J Cell Biol. 1983 Aug;97(2):351–358. doi: 10.1083/jcb.97.2.351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parish C. R., Hogarth P. M., McKenzie I. F. Evidence that Thy-1 and Ly-5 (T-200) antigens interact with sulphated carbohydrates. Immunol Cell Biol. 1988 Jan;66(Pt 3):221–230. doi: 10.1038/icb.1988.28. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parish C. R., Snowden J. M. Lymphocytes express a diverse array of specific receptors for sulfated polysaccharides. Cell Immunol. 1985 Mar;91(1):201–214. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(85)90044-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piepkorn M., Hovingh P., Linker A. Evidence for independent metabolism and cell surface localization of cell surface localization of cellular proteoglycans and glycosaminoglycan free chains. J Cell Physiol. 1988 May;135(2):189–199. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041350206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rapraeger A., Jalkanen M., Endo E., Koda J., Bernfield M. The cell surface proteoglycan from mouse mammary epithelial cells bears chondroitin sulfate and heparan sulfate glycosaminoglycans. J Biol Chem. 1985 Sep 15;260(20):11046–11052. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rider C. C., Hart G. W. Differential sulphation of chondroitins in murine T and B lymphocytes and lymphoma cells. Mol Immunol. 1987 Sep;24(9):963–967. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(87)90007-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanderson R. D., Lalor P., Bernfield M. B lymphocytes express and lose syndecan at specific stages of differentiation. Cell Regul. 1989 Nov;1(1):27–35. doi: 10.1091/mbc.1.1.27. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sant A. J., Cullen S. E., Schwartz B. D. Biosynthetic relationships of the chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan with Ia and invariant chain glycoproteins. J Immunol. 1985 Jul;135(1):416–422. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shively J. E., Conrad H. E. Formation of anhydrosugars in the chemical depolymerization of heparin. Biochemistry. 1976 Sep 7;15(18):3932–3942. doi: 10.1021/bi00663a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steward W. P., Christmas S. E., Lyon M., Gallagher J. T. The synthesis of proteoglycans by human T lymphocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 May 22;1052(3):416–425. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(90)90151-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasteson A. A method for the determination of the molecular weight and molecular-weight distribution of chondroitin sulphate. J Chromatogr. 1971 Jul 8;59(1):87–97. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(01)80009-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]