Abstract
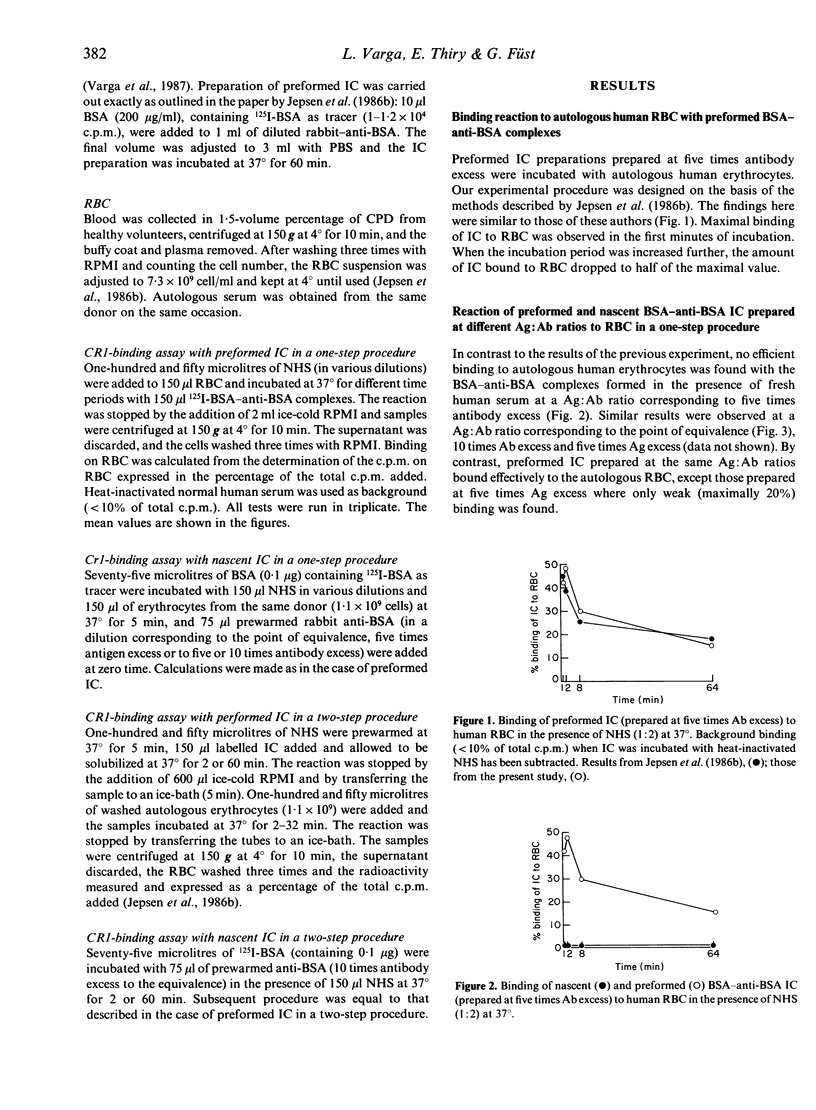
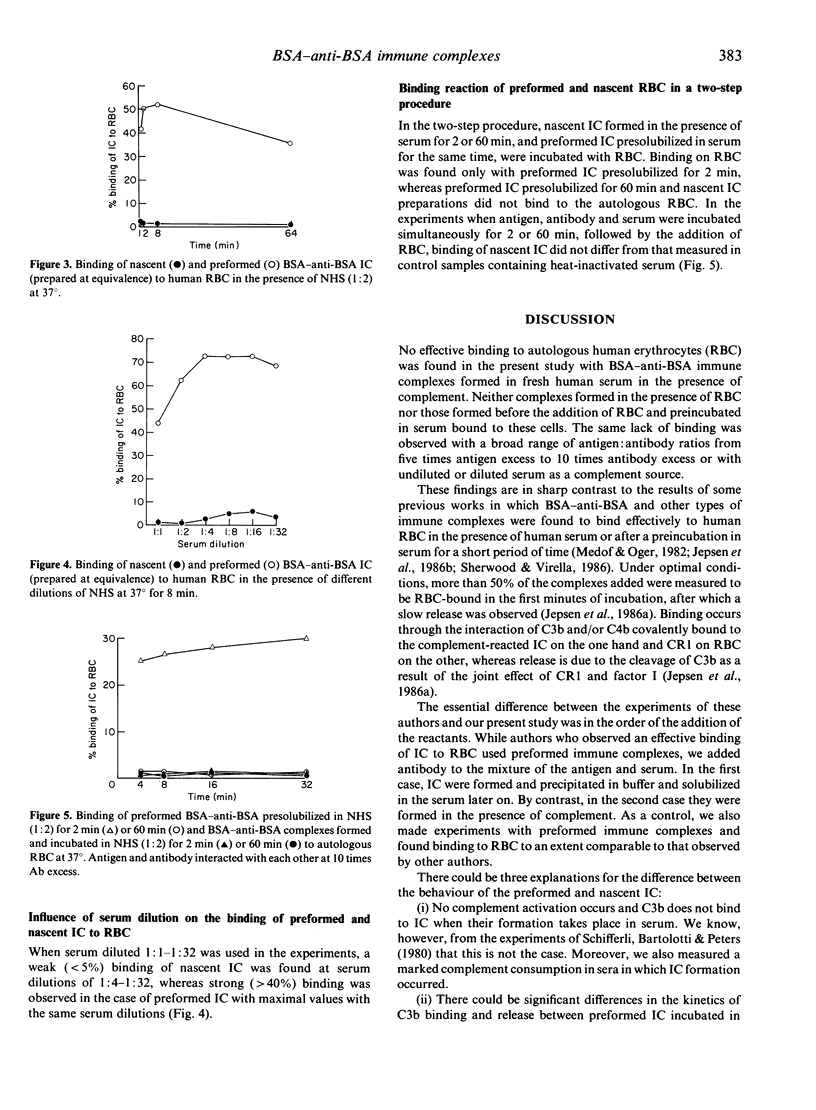
The binding of 125I-BSA-anti-BSA immune complexes (IC) formed in the presence of complement (nascent IC) and those that reacted with complement after their formation (preformed IC) to human erythrocytes was studied. The effect of antigen-antibody ratios and serum dilutions on IC binding to red blood cells (RBC) were also investigated. A dramatic difference was found between the behaviour of the two types of complexes: while preformed IC bound effectively to human RBC after their interaction with complement, no efficient RBC-binding was observed with nascent BSA-anti-BSA complexes formed in the presence of complement. Changing the antigen-antibody ratio or dilution of serum did not affect markedly the extent of difference between the binding of preformed and nascent IC. Our findings do not support the essential role of red blood cells in the elimination of each type of IC.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anh-Tuan N., Falus A., Füst G., Merétey K., Hollán S. R. Appearance of covalently bound antigen in immune complexes formed during the activation of complement. J Immunol Methods. 1984 Dec 31;75(2):257–263. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(84)90109-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cornacoff J. B., Hebert L. A., Smead W. L., VanAman M. E., Birmingham D. J., Waxman F. J. Primate erythrocyte-immune complex-clearing mechanism. J Clin Invest. 1983 Feb;71(2):236–247. doi: 10.1172/JCI110764. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eden A., Miller G. W., Nussenzweig V. Human lymphocytes bear membrane receptors for C3b and C3d. J Clin Invest. 1973 Dec;52(12):3239–3242. doi: 10.1172/JCI107525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ginsberg M. H., Henson P. M. Enhancement of platelet response to immune complexes and IgG aggregates by lipid A-rich bacterial lipopolysaccharides. J Exp Med. 1978 Jan 1;147(1):207–217. doi: 10.1084/jem.147.1.207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henson P. M., Oades Z. G. Stimulation of human neutrophils by soluble and insoluble immunoglobulin aggregates. Secretion of granule constituents and increased oxidation of glucose. J Clin Invest. 1975 Oct;56(4):1053–1061. doi: 10.1172/JCI108152. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jepsen H. H., Svehag S. E., Jarlbaek L., Baatrup G. Interaction of complement-solubilized immune complexes with CR1 receptors on human erythrocytes. The binding reaction. Scand J Immunol. 1986 Jan;23(1):65–73. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1986.tb01943.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jepsen H. H., Svehag S. E., Jensenius J. C., Sim R. B. Release of immune complexes bound to erythrocyte complement receptor (CR1), with particular reference to the role of factor I. Scand J Immunol. 1986 Aug;24(2):205–213. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1986.tb02087.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McConahey P. J., Dixon F. J. A method of trace iodination of proteins for immunologic studies. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1966;29(2):185–189. doi: 10.1159/000229699. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medof M. E., Oger J. J. Competition for immune complexes by red cells in human blood. J Clin Lab Immunol. 1982 Jan;7(1):7–13. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naama J. K., Hamilton A. O., Yeung-Laiwah A. C., Whaley K. Prevention of immune precipitation by purified classical pathway complement components. Clin Exp Immunol. 1984 Nov;58(2):486–492. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naama J. K., Holme E., Hamilton E., Whaley K. Prevention of immune precipitation by purified components of the alternative pathway. Clin Exp Immunol. 1985 Apr;60(1):169–177. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Onyewotu I. I., Holborow E. J., Johnson G. D. Detection and radioassay of soluble circulating immune complexes using guinea pig peritoneal exudate cells. Nature. 1974 Mar 8;248(5444):156–159. doi: 10.1038/248156a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schifferli J. A., Bartolotti S. R., Peters D. K. Inhibition of immune precipitation by complement. Clin Exp Immunol. 1980 Nov;42(2):387–394. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schifferli J. A., Peters D. K. Complement, the immune-complex lattice, and the pathophysiology of complement-deficiency syndromes. Lancet. 1983 Oct 22;2(8356):957–959. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)90464-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherwood T. A., Virella G. The binding of immune complexes to human red cells: complement requirements and fate of the RBC-bound IC after interaction with human phagocytic cells. Clin Exp Immunol. 1986 Apr;64(1):195–204. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegel I., Liu T. L., Gleicher N. The red-cell immune system. Lancet. 1981 Sep 12;2(8246):556–559. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(81)90941-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi M., Tack B. F., Nussenzweig V. Requirements for the solubilization of immune aggregates by complement: assembly of a factor B-dependent C3-convertase on the immune complexes. J Exp Med. 1977 Jan 1;145(1):86–100. doi: 10.1084/jem.145.1.86. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi M., Takahashi S., Brade V., Nussenzweig V. Requirements for the solubilization of immune aggregates by complement. The role of the classical pathway. J Clin Invest. 1978 Aug;62(2):349–358. doi: 10.1172/JCI109135. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varga L., Miszlay Z., Czink E., Pálóczi K., Szegedi G., Füst G., Hollán S. R. Study of the immune complex precipitation-inhibiting capacity of sera of patients with chronic lymphocytic leukaemia. Diagn Clin Immunol. 1987;5(3):129–134. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webb J., Whaley K. Complement and immune complex diseases. Aust N Z J Med. 1986 Apr;16(2):268–278. doi: 10.1111/j.1445-5994.1986.tb01177.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


