Abstract
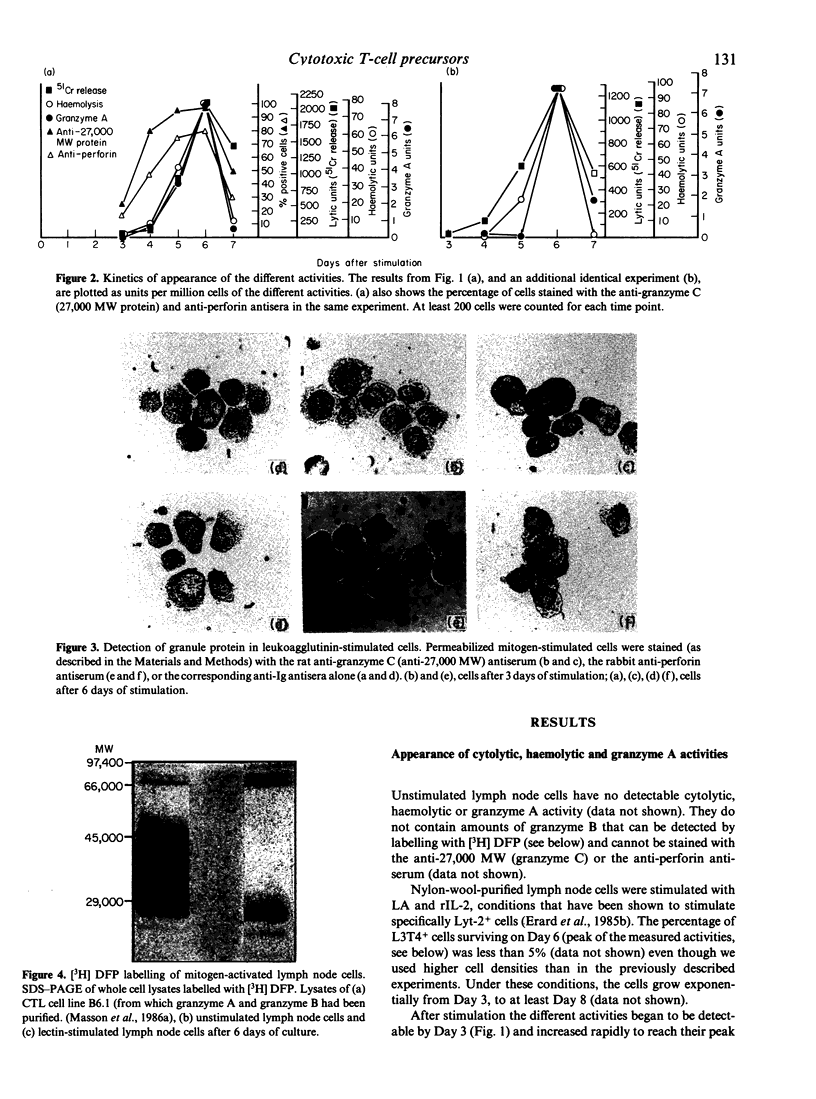
Lysis of target cells by cytolytic T lymphocytes (CTL) is associated with the exocytosis of cytoplasmic granules. Purified granules from CTL cell lines contain a pore-forming protein (perforin), tree serine esterases, granzyme A (60,000 MW), granzyme B (29,000 MW), and granzyme C (27,000 MW). We have compared the kinetics of appearance of cytolytic activity with that of perforin and granzyme A activity during activation of lymphocytes from normal animals with leukoagglutinin (LA) and recombinant interleukin-2 (rIL-2). Unstimulated lymph node cells do not express any of these activities, which appear between Day 3 and Day 4 of stimulation and increase rapidly to reach a pronounced peak on Day 6. On Day 7 all the activities are considerably lower, even though the cells still proliferate exponentially. There is a good correlation between the kinetics of appearance of all of these activities. Using antisera against perforin and against granzyme C, one can detect positive cytoplasmic granules in a small fraction of cells on Day 3; by Day 5, 80-90% of the cells are stained. This proportion decreases again on Day 7.
Full text
PDF




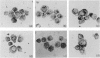
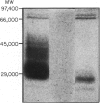
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bevan M. J., Langman R. E., Cohn M. H-2 antigen-specific cytotoxic T cells induced by concanavalin A: estimation of their relative frequency. Eur J Immunol. 1976 Mar;6(3):150–156. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830060303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunet J. F., Dosseto M., Denizot F., Mattei M. G., Clark W. R., Haqqi T. M., Ferrier P., Nabholz M., Schmitt-Verhulst A. M., Luciani M. F. The inducible cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated gene transcript CTLA-1 sequence and gene localization to mouse chromosome 14. Nature. 1986 Jul 17;322(6076):268–271. doi: 10.1038/322268a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devos R., Plaetinck G., Cheroutre H., Simons G., Degrave W., Tavernier J., Remaut E., Fiers W. Molecular cloning of human interleukin 2 cDNA and its expression in E. coli. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Jul 11;11(13):4307–4323. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.13.4307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erard F., Corthesy P., Nabholz M., Lowenthal J. W., Zaech P., Plaetinck G., MacDonald H. R. Interleukin 2 is both necessary and sufficient for the growth and differentiation of lectin-stimulated cytolytic T lymphocyte precursors. J Immunol. 1985 Mar;134(3):1644–1652. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erard F., Nabholz M., Dupuy-D'Angeac A., MacDonald H. R. Differential requirements for the induction of interleukin 2 responsiveness in L3T4+ and Lyt-2+ T cell subsets. J Exp Med. 1985 Nov 1;162(5):1738–1743. doi: 10.1084/jem.162.5.1738. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erard F., Nabholz M., MacDonald H. R. Antigen stimulation of cytolytic T lymphocyte precursors: minimal requirements for growth and acquisition of cytolytic activity. Eur J Immunol. 1985 Aug;15(8):798–803. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830150811. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia-Sanz J. A., Plaetinck G., Velotti F., Masson D., Tschopp J., MacDonald H. R., Nabholz M. Perforin is present only in normal activated Lyt2+ T lymphocytes and not in L3T4+ cells, but the serine protease granzyme A is made by both subsets. EMBO J. 1987 Apr;6(4):933–938. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04841.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gershenfeld H. K., Weissman I. L. Cloning of a cDNA for a T cell-specific serine protease from a cytotoxic T lymphocyte. Science. 1986 May 16;232(4752):854–858. doi: 10.1126/science.2422755. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guesdon J. L., Ternynck T., Avrameas S. The use of avidin-biotin interaction in immunoenzymatic techniques. J Histochem Cytochem. 1979 Aug;27(8):1131–1139. doi: 10.1177/27.8.90074. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardt C., Sato N., Wagner H. Functional and biochemical characteristics of a murine interleukin 2 receptor-inducing factor. Eur J Immunol. 1987 Feb;17(2):209–216. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830170210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henkart P. A. Mechanism of lymphocyte-mediated cytotoxicity. Annu Rev Immunol. 1985;3:31–58. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.03.040185.000335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenne D., Rey C., Masson D., Stanley K. K., Herz J., Plaetinck G., Tschopp J. cDNA cloning of granzyme C, a granule-associated serine protease of cytolytic T lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1988 Jan 1;140(1):318–323. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramer M. D., Binninger L., Schirrmacher V., Moll H., Prester M., Nerz G., Simon M. M. Characterization and isolation of a trypsin-like serine protease from a long-term culture cytolytic T cell line and its expression by functionally distinct T cells. J Immunol. 1986 Jun 15;136(12):4644–4651. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lobe C. G., Havele C., Bleackley R. C. Cloning of two genes that are specifically expressed in activated cytotoxic T lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(5):1448–1452. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.5.1448. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin D. E., Zalman L. S., Jung G., Müller-Eberhard H. J. Induction of synthesis of the cytolytic C9 (ninth component of complement)-related protein in human peripheral mononuclear cells by monoclonal antibody OKT3 or interleukin 2: correlation with cytotoxicity and lymphocyte phenotype. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(9):2946–2950. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.9.2946. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masson D., Corthésy P., Nabholz M., Tschopp J. Appearance of cytolytic granules upon induction of cytolytic activity in CTL-hybrids. EMBO J. 1985 Oct;4(10):2533–2538. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03967.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masson D., Nabholz M., Estrade C., Tschopp J. Granules of cytolytic T-lymphocytes contain two serine esterases. EMBO J. 1986 Jul;5(7):1595–1600. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04401.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masson D., Tschopp J. A family of serine esterases in lytic granules of cytolytic T lymphocytes. Cell. 1987 Jun 5;49(5):679–685. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90544-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masson D., Tschopp J. Isolation of a lytic, pore-forming protein (perforin) from cytolytic T-lymphocytes. J Biol Chem. 1985 Aug 5;260(16):9069–9072. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pasternack M. S., Eisen H. N. A novel serine esterase expressed by cytotoxic T lymphocytes. 1985 Apr 25-May 1Nature. 314(6013):743–745. doi: 10.1038/314743a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pasternack M. S., Verret C. R., Liu M. A., Eisen H. N. Serine esterase in cytolytic T lymphocytes. Nature. 1986 Aug 21;322(6081):740–743. doi: 10.1038/322740a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Podack E. R., Konigsberg P. J. Cytolytic T cell granules. Isolation, structural, biochemical, and functional characterization. J Exp Med. 1984 Sep 1;160(3):695–710. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.3.695. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Podack E. R., Young J. D., Cohn Z. A. Isolation and biochemical and functional characterization of perforin 1 from cytolytic T-cell granules. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(24):8629–8633. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.24.8629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Velotti F., MacDonald H. R., Nabholz M. Granzyme A secretion by normal activated Lyt-2+ and L3T4+ T cells in response to antigenic stimulation. Eur J Immunol. 1987 Aug;17(8):1095–1099. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830170804. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young J. D., Leong L. G., Liu C. C., Damiano A., Cohn Z. A. Extracellular release of lymphocyte cytolytic pore-forming protein (perforin) after ionophore stimulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(15):5668–5672. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.15.5668. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young J. D., Leong L. G., Liu C. C., Damiano A., Wall D. A., Cohn Z. A. Isolation and characterization of a serine esterase from cytolytic T cell granules. Cell. 1986 Oct 24;47(2):183–194. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90441-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]