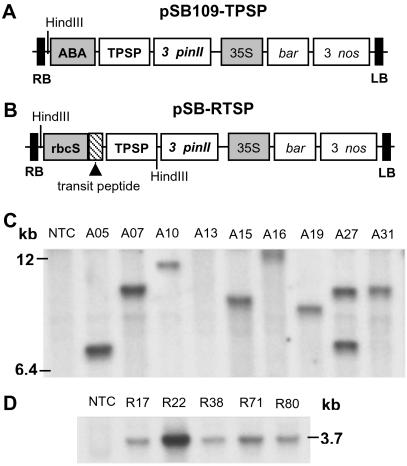
Fig 1.
Schematic representation of the expression vectors and DNA-blot hybridization analysis. Two binary plasmids, each containing the trehalose biosynthetic fusion gene (TPSP) that includes the coding regions of the E. coli otsA and otsB genes (encoding TPS and TPP, respectively), were constructed and transformed into indica rice, as described in Materials and Methods. (A) pSB109-TPSP plasmid. (B) pSB-RTSP plasmid. Shaded boxes represent promoter elements (ABA, ABA-inducible; rbcS, rice rbcS; 35S, cauliflower mosaic virus 35S); RB and LB represent T-DNA border on the right and left sides, respectively. Shown is DNA-blot hybridization analysis from nontransformed control (NTC) plant, and representative transgenic plants of nine A-lines (C) and five R-lines (D) that were transformed with the plasmid pSB109-TPSP and pSB-RTSP, respectively. The rice genomic DNA was digested with HindIII (a unique site in the plasmid pSB109-TPSP, whereas two sites are present in the plasmid pSB-RTSP) and DNA blot hybridization analysis was performed with the 2.2-kb TPSP fusion gene as the probe. Molecular sizes (kb) are indicated.