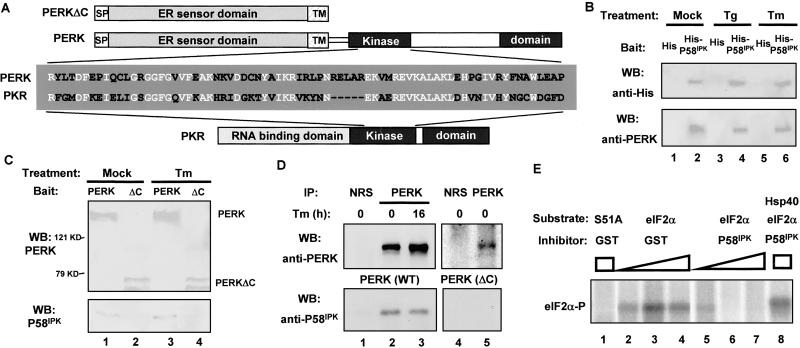
Fig 2.
P58IPK interacts with and inhibits PERK. (A) Schematic diagram for PERK, PERKΔC, and PKR. The P58IPK-interacting region of PKR, located in the kinase domain, was aligned with the corresponding region of PERK. Identical sequences are indicated in white. (B) His-P58IPK pulls down PERK. His-tagged P58IPK (lanes 2, 4, and 6) or His-tag alone (lanes 1, 3, and 5), bound on beads, was incubated with lysates from AR42J cells grown in the absence or presence of thapsigargin (Tg) or tunicamycin (Tm). The bead-bound protein complex was subjected to Western blotting (WB) by using the indicated antibodies. (C) HA-PERK pulls down P58IPK. HA-PERK (lanes 1 and 3) or HA-PERKΔC (lanes 2 and 4) from mock-treated or tunicamycin-treated COS1 cells was used as bait to pull down purified GST-P58IPK. The bead-bound protein complex was subjected to Western blotting by using indicated antibodies. (D) PERK coimmunoprecipitates with P58IPK. COS1 cells cotransfected with P58IPK and PERK (lanes 1–3) or PERKΔC (lanes 4 and 5), either treated with tunicamycin or untreated, were lysed and immunoprecipitated (IP) with anti-PERK antibody (lanes 2, 3, and 5) or normal rabbit serum (NRS, lanes 1 and 4). The precipitates then were subjected to Western blotting by using indicated antibodies. (E) P58IPK inhibits PERK kinase activity. Purified GST-PERK was incubated with purified WT eIF2α (lanes 2–8) or S51A mutant eIF2α (lane 1) and [γ-32P]ATP in the presence of purified GST-P58IPK (lanes 5–8) or GST control (lanes 2–4). Hsp40 was included as a specific inhibitor to P58IPK (lane 8). Reaction mixtures were subjected to SDS/PAGE and visualized by autoradiography.