Abstract
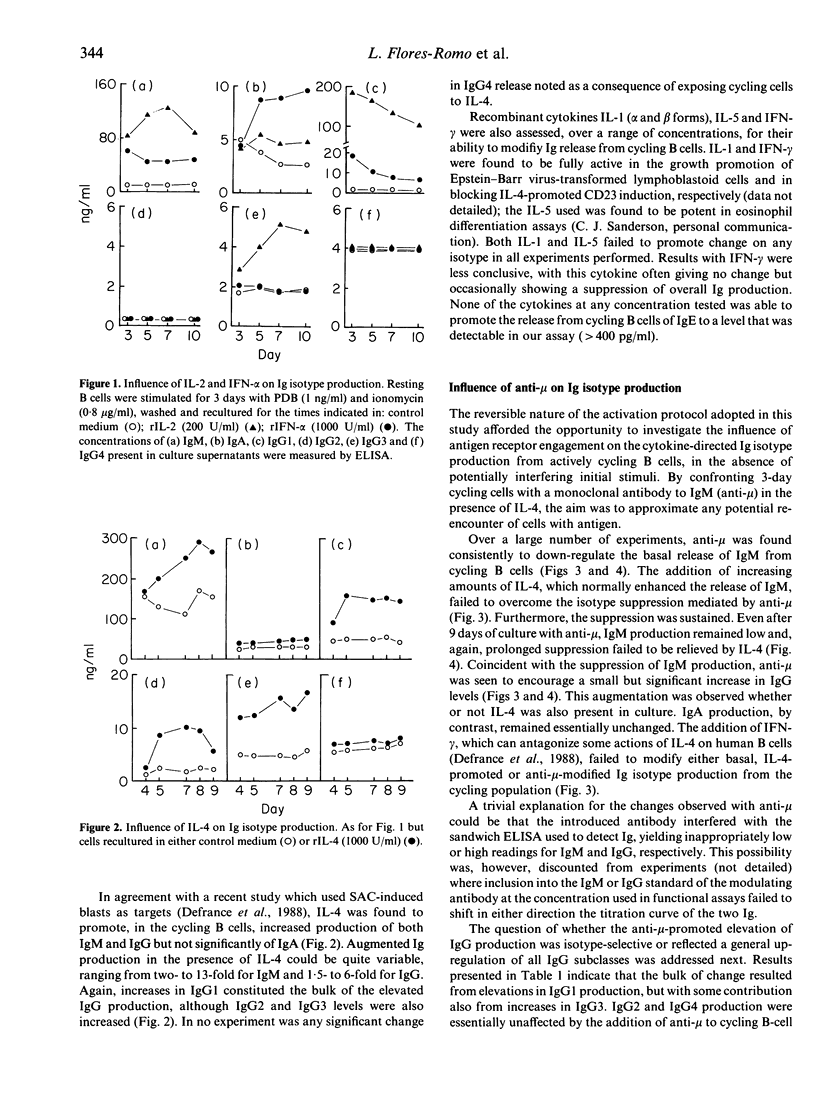
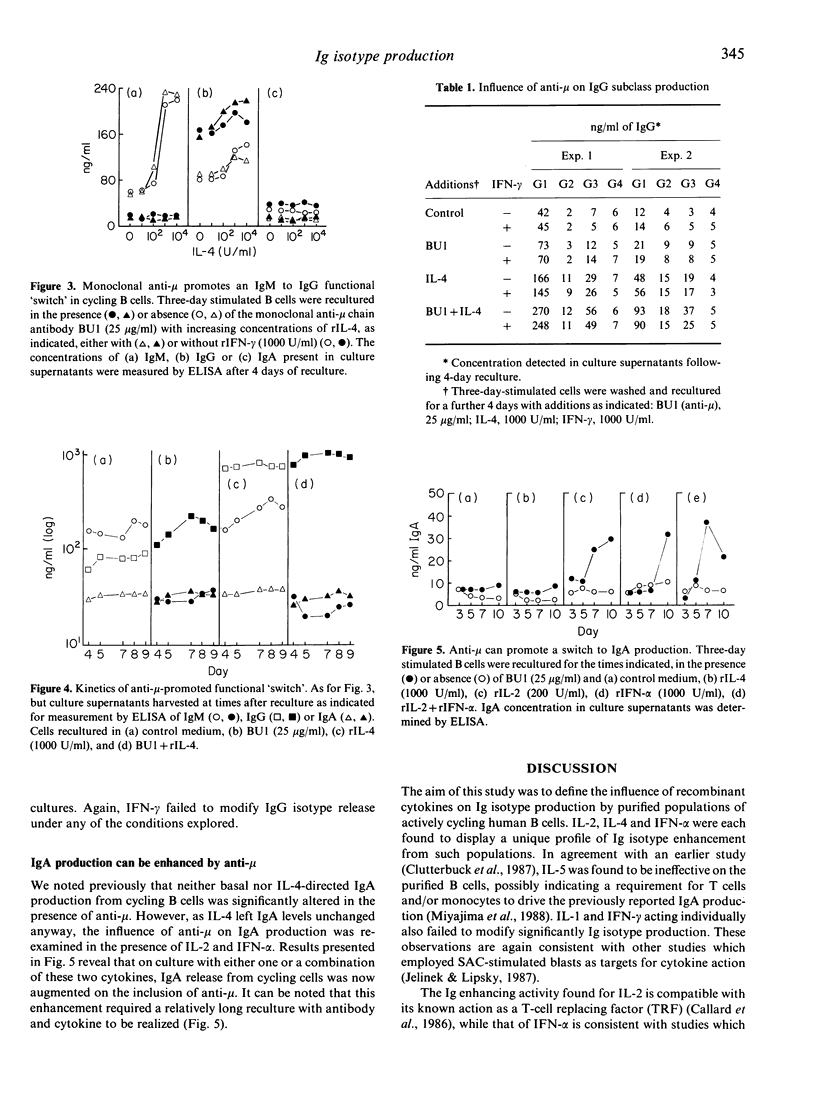
Actively cycling populations of purified human tonsilar B lymphocytes were examined for their capacity to secrete IgM, IgA, IgE and IgG of all four subclasses in direct response to recombinant cytokines; in some experiments, monoclonal antibody to IgM (anti-mu) was included in order to explore the influence of antigen receptor ligation on immunoglobulin (Ig) production. Enhanced IgM release was seen on culture of the cycling cells with either interleukin-2 (IL-2), IL-4 or interferon-alpha (IFN-alpha). IL-2 and IFN-alpha also augmented IgA production, whereas IL-4 had no effect on this isotype. IL-4 did, however, encourage the production of the IgG subclasses IgG1, IgG2 and IgG3, while IL-2 augmented IgG1 and IgG3 release and IFN-alpha increased IgG1 levels. IgG4 production, and that of IgE, failed to be perturbed by any of the cytokines assayed. Neither IL-1 alpha, IL-1 beta, IL-5 nor IFN-gamma significantly altered the profile of Ig isotype release. When confronted with anti-mu, cycling B cells demonstrated a marked suppression in IgM production. Suppression could not be overcome by the addition to culture of the normally IgM-promoting IL-4. Concomitant with the reduction in IgM levels, an increase in IgG release was observed. This was comprised of elevations in IgG1 and IgG3. Although not influencing IgA release directly, anti-mu was found to promote increased IgA production in co-culture with either IL-2 or IFN-alpha. The findings are discussed in the context of recent findings on Ig isotype control in both human and murine systems.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abbas A. K., Klaus G. G. Inhibition of antibody production in plasmacytoma cells by antigen. Eur J Immunol. 1977 Oct;7(10):667–674. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830071003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Callard R. E., Smith S. H., Shields J. G., Levinsky R. J. T cell help in human antigen-specific antibody responses can be replaced by interleukin 2. Eur J Immunol. 1986 Sep;16(9):1037–1042. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830160902. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clutterbuck E., Shields J. G., Gordon J., Smith S. H., Boyd A., Callard R. E., Campbell H. D., Young I. G., Sanderson C. J. Recombinant human interleukin 5 is an eosinophil differentiation factor but has no activity in standard human B cell growth factor assays. Eur J Immunol. 1987 Dec;17(12):1743–1750. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830171210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Defrance T., Vanbervliet B., Pène J., Banchereau J. Human recombinant IL-4 induces activated B lymphocytes to produce IgG and IgM. J Immunol. 1988 Sep 15;141(6):2000–2005. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flores-Romo L., Foster D., Guy G. R., Gordon J. Phorbol ester and calcium ionophore are sufficient to promote cell replication in cultures of quiescent human B lymphocytes. Immunology. 1989 Feb;66(2):228–232. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon J., Millsum M. J., Flores-Romo L., Gillis S. Regulation of resting and cycling human B lymphocytes via surface IgM and the accessory molecules interleukin-4, CD23 and CD40. Immunology. 1989 Dec;68(4):526–531. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon J., Millsum M. J., Guy G. R., Ledbetter J. A. Synergistic interaction between interleukin 4 and anti-Bp50 (CDw40) revealed in a novel B cell restimulation assay. Eur J Immunol. 1987 Oct;17(10):1535–1538. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830171026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jefferis R., Reimer C. B., Skvaril F., de Lange G., Ling N. R., Lowe J., Walker M. R., Phillips D. J., Aloisio C. H., Wells T. W. Evaluation of monoclonal antibodies having specificity for human IgG sub-classes: results of an IUIS/WHO collaborative study. Immunol Lett. 1985;10(3-4):223–252. doi: 10.1016/0165-2478(85)90082-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jelinek D. F., Lipsky P. E. Enhancement of human B cell proliferation and differentiation by tumor necrosis factor-alpha and interleukin 1. J Immunol. 1987 Nov 1;139(9):2970–2976. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jelinek D. F., Lipsky P. E. The role of B cell proliferation in the generation of immunoglobulin-secreting cells in man. J Immunol. 1983 Jun;130(6):2597–2604. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maruyama S., Kubagawa H., Cooper M. D. Activation of human B cells and inhibition of their terminal differentiation by monoclonal anti-mu antibodies. J Immunol. 1985 Jul;135(1):192–199. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyajima A., Miyatake S., Schreurs J., De Vries J., Arai N., Yokota T., Arai K. Coordinate regulation of immune and inflammatory responses by T cell-derived lymphokines. FASEB J. 1988 Jun;2(9):2462–2473. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.2.9.2836253. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paul W. E. Interleukin 4/B cell stimulatory factor 1: one lymphokine, many functions. FASEB J. 1987 Dec;1(6):456–461. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.1.6.3315808. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pluschke G., Bordmann G., Daoudaki M. E., Lambris J. D., Achtman M., Neibert M. Isolation of rat IgM to IgG hybridoma isotype switch variants and analysis of the efficiency of rat Ig in complement activation. Eur J Immunol. 1989 Jan;19(1):131–135. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830190121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sidman C. L., Marshall J. D. B cell maturation factor: effects on various cell populations. J Immunol. 1984 Feb;132(2):845–850. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snapper C. M., Finkelman F. D., Paul W. E. Differential regulation of IgG1 and IgE synthesis by interleukin 4. J Exp Med. 1988 Jan 1;167(1):183–196. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.1.183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Symons D. B., Clarkson C. A., Hall F. J. Soluble and immobilized anti-Ig antibodies in the regulation of LPS-induced lymphoblasts. Immunology. 1985 Jan;54(1):71–78. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thyphronitis G., Tsokos G. C., June C. H., Levine A. D., Finkelman F. D. IgE secretion by Epstein-Barr virus-infected purified human B lymphocytes is stimulated by interleukin 4 and suppressed by interferon gamma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(14):5580–5584. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.14.5580. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


