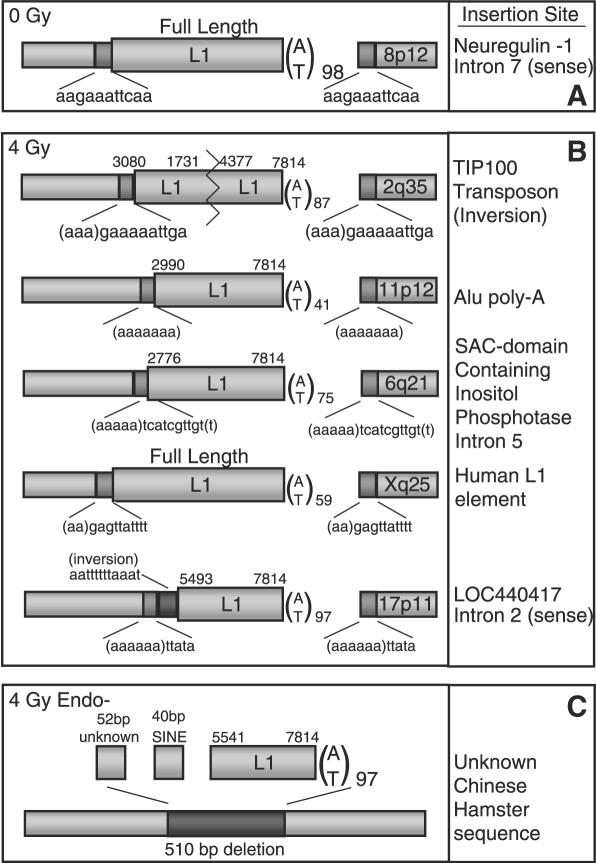
Figure 5.
L1 insertions from irradiated clones have endonuclease-dependent features. Single L1-EGFP transfected 143B cells expressing EGFP were isolated by flow cytometry and expanded. DNA was extracted and the 3′ genomic flank amplified and sequenced by suppression PCR or inverse PCR (see Materials and Methods). The 5′ flank was then amplified and sequenced using primers designed from the human genome database. Hallmarks of endonuclease-dependent L1 insertion include 7–20 bp target site duplications (TSDs), AT rich consensus target sites and poly-A tails. Dark gray boxes denote TSDs. TSD sequences are displayed beneath each dark gray box. Numbers represent map positions in L1-EGFP; a full length insertion (including the spliced EGFP cassette) is 7814 bp long. Poly-A tail length is given as the subscripted number next to A/T. Chromosome insertion location is given in the 3′ flank. (A) L1 insertion flanks from an unirradiated cell. (B) Insertion flanks recovered following 4 Gy irradiation resemble most endonuclease-dependent genomic L1 insertions. (C) An endonuclease-deficient L1 insertion in a CHO-K1 cell has a deletion at the site of insertion, lacks target site duplications and has 5′ transduced sequence.