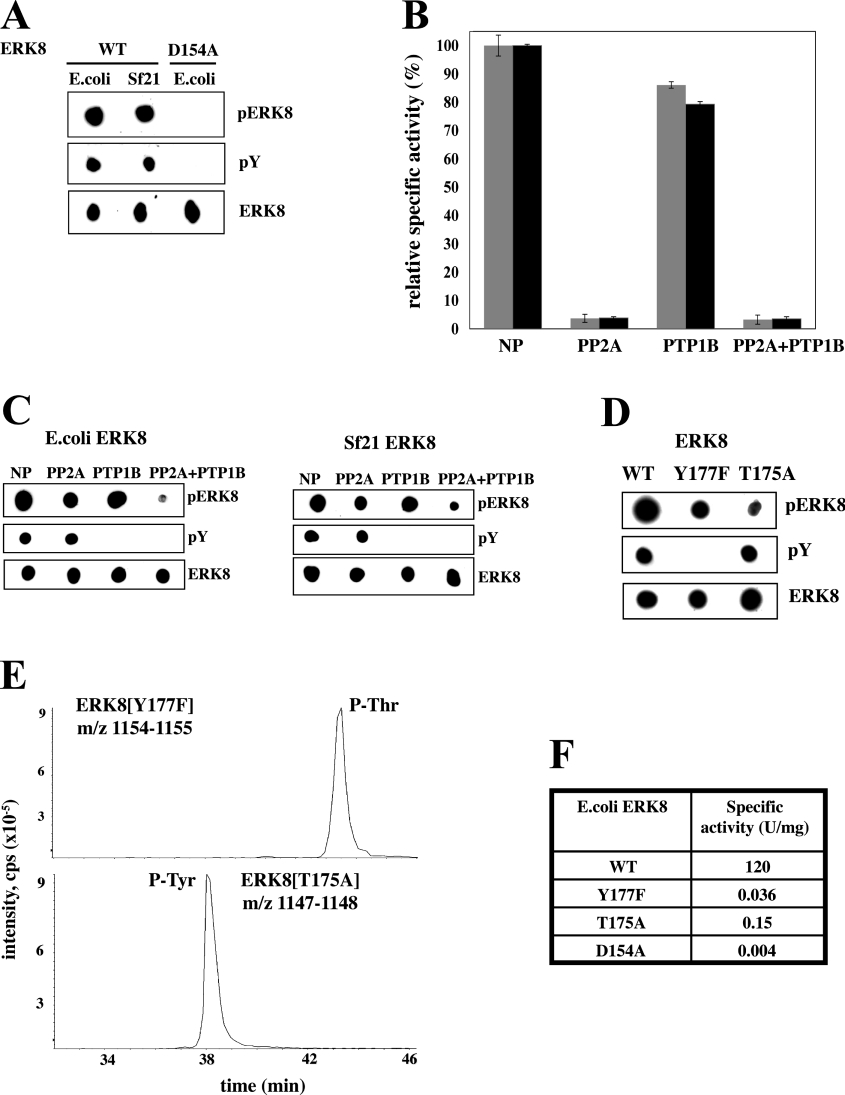
Figure 1. State of phosphorylation of the activation loop of ERK8 and effect of phosphatases.
Wild-type (WT) ERK8, and the catalytically inactive D154A mutant were expressed as GST fusions in E. coli and His6-tagged WT ERK8 was expressed in Sf21 cells. (A) The purified proteins (100 ng) were spotted on to nitrocellulose membranes and immunoblotted using the ECL® detection system (Amersham Pharmacia Biotech, Little Chalfont, U.K.). The antibodies used were a phosphospecific antibody that recognizes the phosphorylated Thr-Glu-Tyr motif of ERK1 and ERK2, but also recognizes the same region in ERK8 (pERK8), an anti-phosphotyrosine antibody (pY), and an antibody that recognizes phosphorylated and unphosphorylated ERK8 equally well (ERK8). (B) Wild-type GST–ERK8 (grey bars) or His6–ERK8 (black bars) were incubated with PP2A, PTP1B, both phosphatases or in the absence of any phosphatase (NP; no phosphatase) as described in the Materials and methods section. Aliquots of each reaction were then assayed for ERK8 activity using MBP as a substrate. (C) Further aliquots of the incubations from (B) were spotted on to nitrocellulose membranes and immunoblotted with the antibodies used in (A). (D) The experiment was carried out as in (A), except that the ERK8[T175A] and the ERK8[Y177F] mutants were used, as well as the wild-type enzyme. (E) MS analysis of tryptic digests of ERK8[Y177F] and ERK8[T175A] showing the extracted ion chromatograms for the doubly charged ([M−2H]2−) tryptic phosphopeptide ions. Upper panel: the peptide comprising Ser-161–Arg-182 of ERK8[Y177F] (m/z=1154–1155); lower panel: the peptide comprising Ser-161–Arg-182 of ERK8[T175A] (m/z=1147–1148). (F) The specific activities of wild-type ERK8, ERK8[Y177F], ERK8[T175A] and ERK8[D154A] were determined using MBP as substrate. Protein concentrations were determined by the method of Bradford.