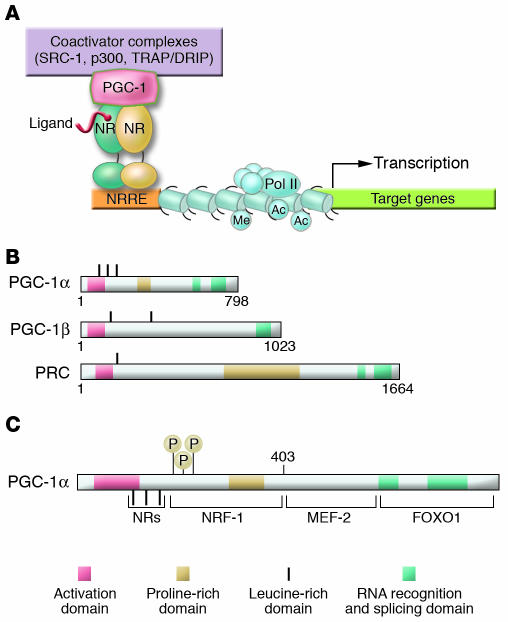
Figure 1.
The PGC-1 coactivator family: inducible boosters of gene transcription. (A) The schematic uses generic NRs as an example of how inducible PGC-1 coactivators dock to transcription factor targets and recruit protein complexes that activate transcription via either enzymatic modification of chromatin, such as histone acetylation (e.g., by steroid receptor coactivator-1 [SRC-1] or p300), or direct interaction with the transcription initiation machinery (e.g., the thyroid hormone receptor–associated protein/vitamin D receptor–interacting protein [TRAP/DRIP] coactivator complex). The NR binds cognate NR response elements (NRREs) within the promoter region of the target gene. Specific histone modifications, including acetylation (Ac) and methylation (Me), are shown, as is the RNA polymerase II (Pol II) complex. (B) The schematic depicts the relative length and shared domains of the 3 members of the PGC-1 coactivator family. The nature of the domains is indicated in the key. (C) A schematic of the PGC-1α molecule is shown to denote several key functional domains involved in the interaction with specific target transcription factors including NRs, nuclear respiratory factor-1 (NRF-1), MEF-2, and FOXO1. MAPK phosphorylation (P) sites are also shown.