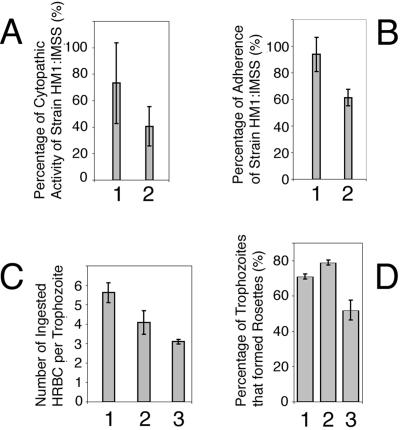
Figure 7.
Virulence and adherence assays. (A) Cytopathic activity measuring the in vitro ability of amoebae to destroy a monolayer of BHK cells. The columns show the average measurements of cytopathic activity from five independent experiments for transfectants 1, pCONTROL and 2, pN-TRUNC as a percentage of the activity of nontransfected HM1:IMSS (in the vertical axis). Bars, SEs. Statistical significance was determined by single-tailed t test (p < 0.05). (B) Adherence ability of trophozoites to a formaldehyde-fixed monolayer of BHK cells. The columns show the average measurements of adhesion from four experiments for transfectants 1, pCONTROL and 2, pN-TRUNC as a percentage of the adhesion ability exhibited by nontransfected HM1:IMSS (in the vertical axis). Bars, SEs. Statistical significance was determined by single-tailed t test (p < 0.005). (C) Erythrophagocytosis assay, measuring the in vitro ability of amoebic trophozoites to ingest human red blood cells (HRBC). The columns show the average number of HRBC internalized by trophozoites during the incubation period (in the vertical axis). Bars, SEs. Statistical significance was determined by single-tailed t test (p < 0.05). 1, Nontransfected strain HM1:IMSS; 2, transfectant pCONTROL; and 3, transfectant pN-TRUNC. (D) Percentage of trophozoites (from 100 trophozoites analyzed) that formed rosettes with HRBC. Bars, SEs. Statistical significance was determined by single-tailed t test (p < 0.05). 1, Nontransfected strain HM1:IMSS; 2, transfectant pCONTROL; and 3, transfectant pN-TRUNC.