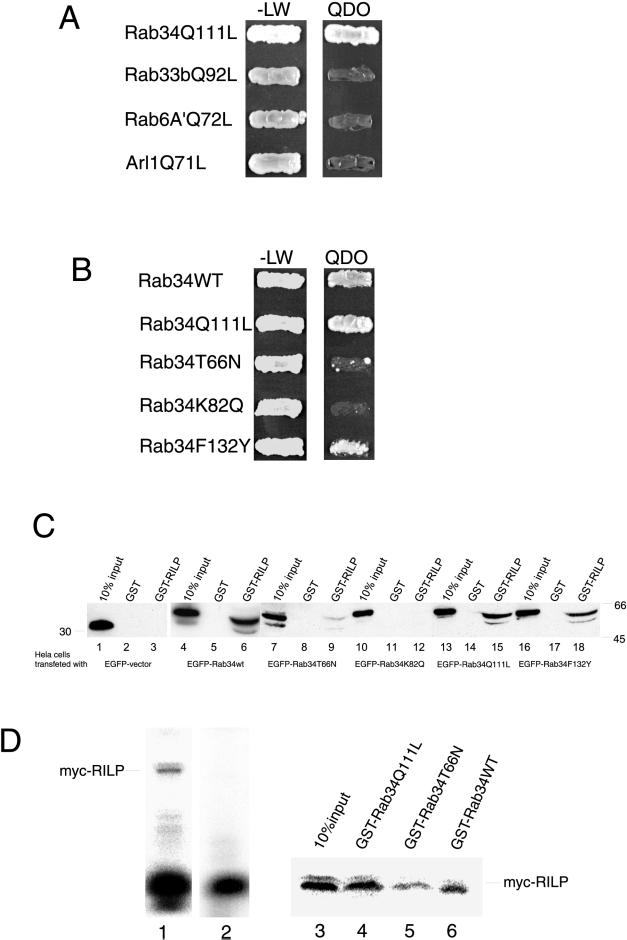
Figure 6.
RILP is an effector of Rab34. (A) Using Rab34Q111L as bait in a yeast two-hybrid system to screen a human kidney cDNA library, a partial coding region of RILP (residues 103–401) was identified. AH109 yeast cells expressing pGBKT7-Rab34Q111L, pGBKT7-Rab33bQ92L, pGBKT7-Rab6A′Q72L, or pGBKT7-Arl1Q71L were mated with Y187 yeast cells expressing pACT2-RILP(103–401). The diploids were grown on SD/-Leu/-Trp (-LW) or SD/-Leu/-Trp/-His/-Ade (QDO) plates. As shown, RILP specifically interacts with GTP-restricted form of Rab34 but not with Rab33b, Rab6A′, or Arl1, three other small GTPases associated with Golgi apparatus. (B) The interaction between Rab34 and RILP is preferential for the wild-type and GTP-restricted form and is dependent on K82 but not F132. AH109 yeast cells expressing pGBKT7-Rab34WT, pGBKT7-Rab34Q111L, pGBKT7-Rab34T66N, pGBKT7-Rab34K82Q, or pGBKT7-Rab34F132Y were mated with Y187 yeast cells expressing pACT2-RILP(103–401). The diploids were grown on either -LW or QDO plates. (C) In vitro binding assay showing K82-dependent preferential interaction of RILP with wild-type and GTP-restricted form of Rab34. Hela cells were transfected with EGFP-vector (lanes 1–3), EGFP-Rab34wt (lanes 4–6), EGFP-Rab34T66N (lanes 7–9), EGFP-Rab34K82Q (lanes 10–12), EGFP-Rab34Q111L (lanes 13–15), and EGFP-Rab34F132Y (lanes 16–18). The resulting cell lysates were incubated with GST-RILP(103–394) or GST, as indicated, coupled to GST-Sepharose 4B resin in the presence of 100 μM GTP-γ-S (or GDP for Rab34T66N) during the binding experiments. Proteins retained on the beads were resolved by SDS-PAGE (along with 10% of starting materials) and then processed for immunoblotting analysis using an mAb against GFP. As shown, EGFP-Rab34wt, EGFP-Rab39Q111L, and EGFP-Rab34F132Y but not others were efficiently retained (∼5–10% of total input) by immobilized RILP but not GST. Less than 1% of the GDP-restricted form of Rab34 (lane 7–9) was retained by the GST-RILP beads. (D) Direct interaction between RILP and Rab34. 35S-Met–labeled myc-RILP was generated by in vitro translation (lane 1, 10 μl of in vitro translation reaction). After immunoprecipitation with myc antibodies, labeled RILP was efficiently depleted (lane 2; 10 μl of in vitro translation reaction after immunoprecipitation). The immunopurified RILP was incubated with immobilized GST-Rab34Q111L (lane 4), GST-Rab34T66N (lane 5), or GST-Rab34wt (lane 6). The amounts of 35S-Met–labeled myc-RILP retained by these beads, together with 10% input (lane 3), were resolved by SDS-PAGE and revealed by PhosphorImager.