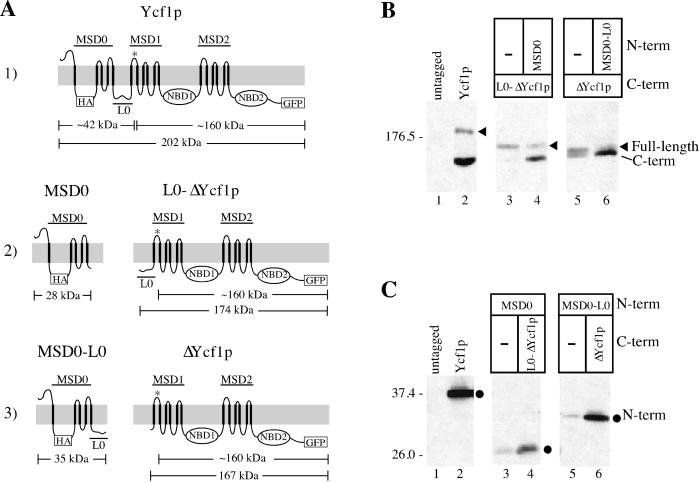
Figure 5.
Coexpression of Ycf1p partial molecules is required for the proteolytic processing and stability of Ycf1p. (A) Schematics of the Ycf1p partial molecules are shown. The N-terminal molecules contain a 3xHA epitope tag at residue 63 in the first cytosolic loop and the C-terminal molecules have GFP fused to the C terminus immediately before the stop codon of Ycf1p. The predicted cleavage site is indicated by an asterisk (*) in all of the C-terminal molecules. The approximate molecular weight of the N- and C-terminal epitope-tagged partial molecules and cleavage products based on SDS-PAGE migration are also shown. Row 1: wild-type Ycf1p-HA-GFP. Row 2: MSD0 includes the N-terminal portion of Ycf1p from amino acids 1–208; L0-ΔYcf1p contains the core region of Ycf1p plus the linker region (L0) from amino acids 209-1515. Row 3: MSD0-L0 represents the N-terminal region from amino acids 1–271; ΔYcf1p includes the core domain from amino acids 272-1515. (B and C) Immunoblot analysis of the C- and N-terminal partial molecules, respectively, expressed alone (−) or coexpressed with their corresponding partial molecules. The full-length protein encoded by each construct is indicated by an arrowhead. As indicated by SDS-PAGE mobility, the C-terminal cleavage product seems to be the same size in all cases and is indicated. The N-terminal partial molecules are indicated by circles. Crude yeast cell extracts (0.4 OD600 cell equivalents per lane) were resolved by either 8% (B) or 10% (C) SDS-PAGE and transferred to nitrocellulose. The C- and N-terminal partial molecules were detected with mouse anti-GFP monoclonal antibodies (B) and rat anti-HA monoclonal antibodies (C), respectively. Molecular weight markers are indicated. The strains used are SM4517 (lane 1), SM4542 (lane 2), SM4741 (lane 4), and SM4742 (lane 6) (B and C); SM4766 (lane 3) and SM4767 (lane 5) (B); and SM4735 (lane 3) and SM4736 (lane 5) (C).