Fig. 4.
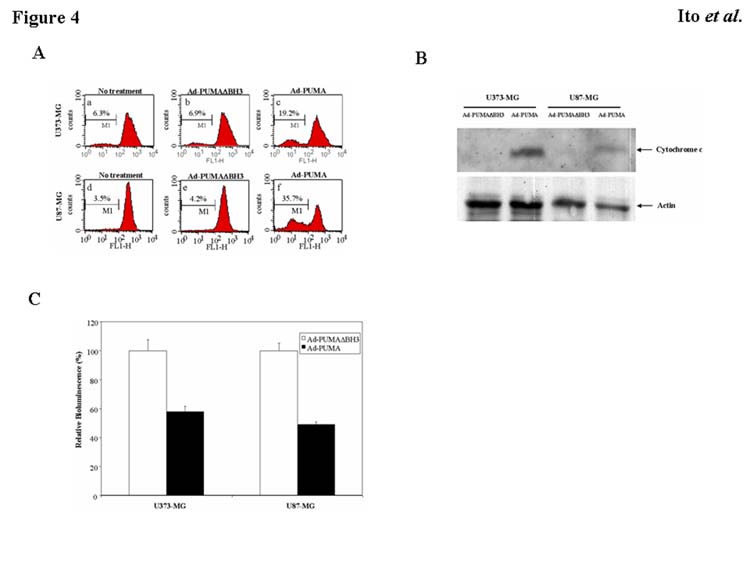
Mechanisms of PUMA-induced apoptosis. A: Disruption of mitochondrial membrane potential in malignant glioma cells by overexpression of PUMA. Rhodamine 123 was used to determine changes in mitochondrial membrane potential using FACS analysis. After treatment with Ad-PUMA or Ad-PUMAΔBH3 at an MOI of 20 for 24 h, attached and detached U373-MG and U87-MG cells were collected and stained with rhodamine 123. B: Release of cytochrome c into cytosol by Ad-PUMA. U373-MG and U87-MG cells were infected with Ad-PUMA or Ad-PUMAΔBH3 at 20 MOI for 24 h. Cytosolic extracts were used for Western blots to assess release of cytochrome c. Actin serves as a loading control. C: Activation of caspase-3 by Ad-PUMA. Activity of caspase-3 in U373-MG and U87-MG cells infected with Ad-PUMA or Ad-PUMAΔBH3 at an MOI of 20 for 24 h was measured with the CleavaLite™ Caspase-3 activity assay kit. Results shown are the mean ± SD of three independent experiments.
