Figure 4.
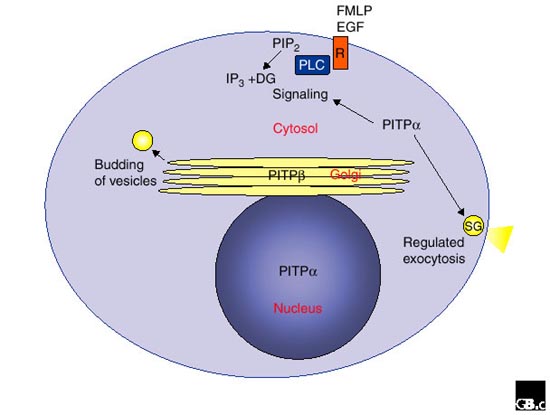
Functions and location of PITPα and PITPβ. PITPα is primarily localized in the cytosol and the nucleus. The major functions of PITP α to be identified are in phospholipase-C-mediated hydrolysis of phosphatidylinositol bisphosphate (PIP2) and in maintaining a pool of PIP2 for exocytosis. PITPβ is primarily localized in the Golgi and the cytosol, and it is involved in the budding of vesicles by making available a pool of phosphoinositides. Abbreviations: DG, diacylglycerol; EGF, epidermal growth factor; FMLP, N-formyl-methionyl-leucyl-phenylalanine; IP3, inositol-1,4,5-trisphosphate; PLC, phospholipase C; R, receptor for EGF and FMLP; SG, secretory granule.
