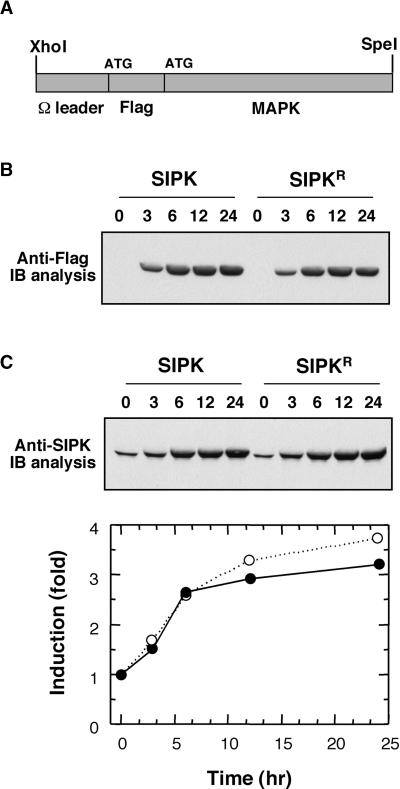
Figure 1.
Expression of SIPK and Its Inactive Mutant under the Control of a Steroid-Inducible Promoter.
(A) A simplified map of MAPK constructs in pTA7002 vector. SIPK or its mutant was inserted into the XhoI–SpeI sites of the steroid-inducible pTA7002 binary vector. The 5′ untranslated region of SIPK was replaced with the Ω sequence from Tobacco mosaic virus. To facilitate the detection of transgene expression, a Flag tag was added to the N terminus of SIPK.
(B) Induction of transgene expression. Tobacco leaves were infiltrated with Agrobacterium carrying SIPK or its inactive mutant with K90 replaced by R (SIPKR). DEX (30 μM) was infiltrated 48 hr later, and samples were taken at the times indicated. The expression of transgenes was monitored by immunoblot (IB) analysis using anti-Flag antibody.
(C) Relative levels of transgene expression in leaves under induced conditions. The levels of SIPK protein in leaves were determined by immunoblot analysis using anti-SIPK antibody. The relative amount of Flag-tagged SIPK (closed circles) or Flag-tagged SIPKR (open circles) versus endogenous SIPK was quantified using NIH Image software (National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, MD). The endogenous SIPK level before induction was normalized to 1.