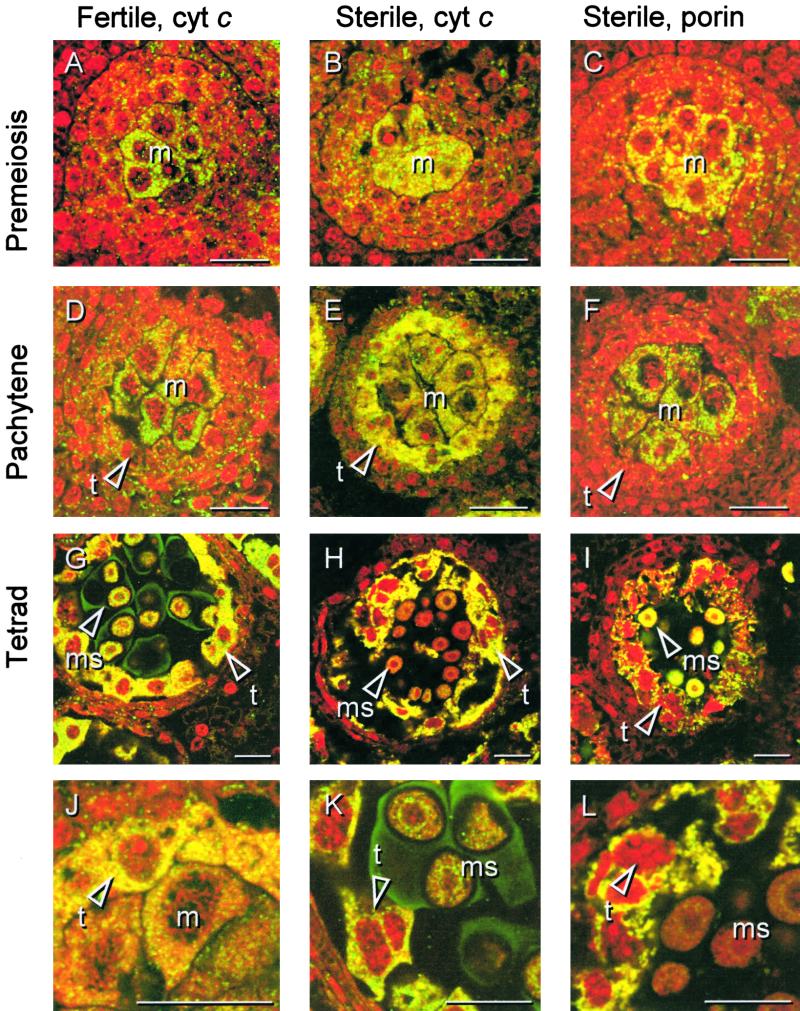
Figure 5.
Immunolocalization of Cytochrome c in Florets of the Fertile and Sterile Sunflower Lines.
Three stages of anther development in the fertile line were compared with the corresponding stages in the sterile line with respect to the in situ localization of cytochrome c. Thin sections from PEG-embedded plant material were labeled with monoclonal antibodies against rat cytochrome c or, as depicted for the sterile line only, with monoclonal antibodies against porin, an integral outer mitochondrial membrane protein. The sections were secondarily labeled with a FITC-conjugated antibody (yellow/green), and nucleic acids were stained with propidium iodide (red) to facilitate identification of the developmental stage.
(A), (B), and (C) Premeiosis.
(D), (E), and (F) Pachytene.
(G), (H), and (I) Tetrad stage.
(A), (D), and (G) show localization of cytochrome c during anther development in the fertile line. (B), (E), and (H) show localization of cytochrome c during anther development in the sterile line. (C), (F), and (I) show localization of porin during anther development in the sterile line.
(J) Subcellular localization of cytochrome c in the sterile line at pachytene shown at higher magnification.
(K) Cytochrome c localization and propidium iodide staining in the fertile line at the tetrad stage shown at higher magnification. The arrowhead points to the chromatin of a tapetal cell.
(L) Cytochrome c localization and propidium iodide staining in the sterile line at the tetrad stage shown at higher magnification. The arrowhead points to the chromatin of a dying tapetal cell.
cyt c, cytochrome c; m, meiocyte(s); t, tapetal cell(s); ms, microspore(s). Bars = 20 μm.