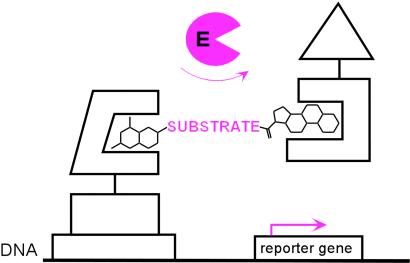
Fig 1.
Chemical complementation. A reaction-independent complementation assay for enzyme catalysis based on the yeast three-hybrid assay. A heterodimeric small molecule bridges a DNA-binding domain–receptor fusion protein and an activation domain–receptor fusion protein, activating transcription of a downstream reporter gene in vivo. Enzyme catalysis of either cleavage or formation of the bond between the two small molecules can be detected as a change in transcription of the reporter gene. The assay can be applied to new chemical reactions simply by synthesizing small molecules with different substrates as linkers and adding an enzyme as a fourth component to the system.