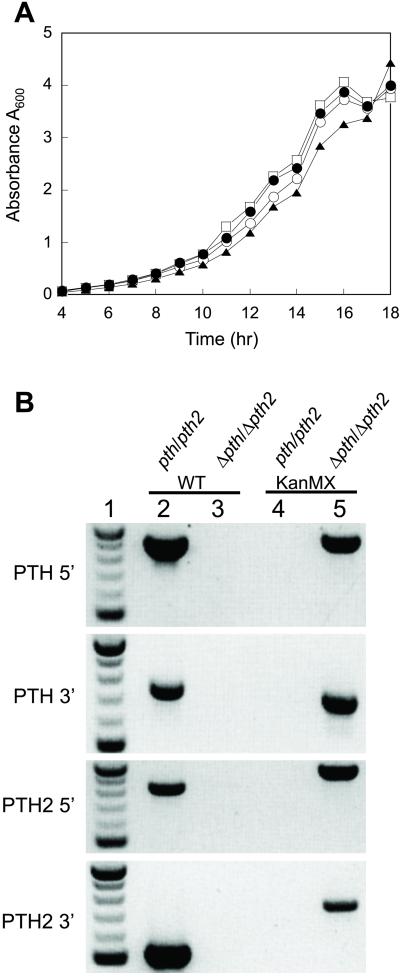
Fig 4.
(A) Growth of S. cerevisiae strains with pth and pth2 genes deleted. Yeast strains with pth (○), pth2 (•), and pth, pth2 (▴) genes deleted were compared with the growth of the parental wild-type strain (□) at 30°C. (B) Confirmation of the genotype of the Δpth/Δpth2 double deletion strain by PCR. Negative image of 1.5% agarose gels stained with ethidium bromide. Lane 1 contains a DNA size marker in 100-bp increments from 500 bp to 1 kb. Lanes 2 and 4 show colony PCR products of the wild-type (pth/pth2) strain, and lanes 3 and 5 show PCR results for the double deletion strain (Δpth/Δpth2). Each intact or knockout allele is verified at both the 5′ and 3′ ends of the gene by using four unique primers (see Materials and Methods). ORF specific primers (PTH 5′, PTH 3′, PTH2 5′, and PTH2 3′) used in combination with two internal primers for each wild-type ORF (WT) or the KanMX deletion cassette produce a PCR product when the wild-type ORF is intact or deleted, respectively.