Table 1.
Summary of sulfated and r-sulfur-containing molecules found in M. tuberculosis and M. smegmatis
| m/z 32S | m/z 34S | Shift in ΔcysH | HSO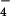 ion observed in MS/MS ion observed in MS/MS |
Form of sulfur | Metabolite annotations | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M. tuberculosis | 421.07 | 423.06 | Y | Y | Sulfate | Trehalose-2-sulfate |
| 485.14 | 487.13 | N | N | r-sulfur | Mycothiol | |
| 881.57 | 883.57 | Y | Y | Sulfate | None | |
| 1,277.97 | 1,279.97 | Y | — | Sulfate | SL-1 precursor | |
| 2,543.22 | 2,545.21 | Y | Y | Sulfate | SL-1 | |
| M. smegmatis | 421.07 | 423.06 | Y | Y | Sulfate | Trehalose-2-sulfate |
| 485.14 | 487.13 | N | N | r-sulfur | Mycothiol | |
| 521.12 | 523.12 | N | N/A | r-sulfur | None | |
| 583.13 | 585.12 | N | N/A | r-sulfur | None | |
| 597.14 | 599.14 | N | N/A | r-sulfur | None | |
| 632.20 | 634.20 | N | N/A | r-sulfur | None | |
| 639.19 | 641.18 | Y | Y | Sulfate | None | |
| 753.23 | 755.22 | N | N/A | r-sulfur | None | |
| 1,009.25 | 1,013.24 | N | N/A | r-sulfur | Mycothiol dimer |
Unless otherwise noted, masses given are monoisotopic and from negative ion mode acquisitions. All ions were singly charged. The resolution was >30,000 for all reported masses.
Name or structure assigned to the metabolite.
Assignment made in this study.
Ion containing a reduced form of sulfur, either a thioether or a thiol.
Due to low abundance, we were unable to perform MS/MS on this ion.
Calculations show this ion likely corresponds to a specific diacylated trehalose-2-sulfate (see text).
Monoisotopic mass of a major lipoform. It should be noted that the calculated mass of the originally proposed SL-1 structure does not match with our measured mass of the SL-1 standard. The standard used for our analysis is of the same batch used to elucidate the structure of SL-1.
Not applicable; MS/MS not performed on r-sulfur-containing compounds, with the exception of mycothiol.
This ion observed in positive mode.
Two mycothiol molecules linked by a disulfide bond, potassiated adduct.
