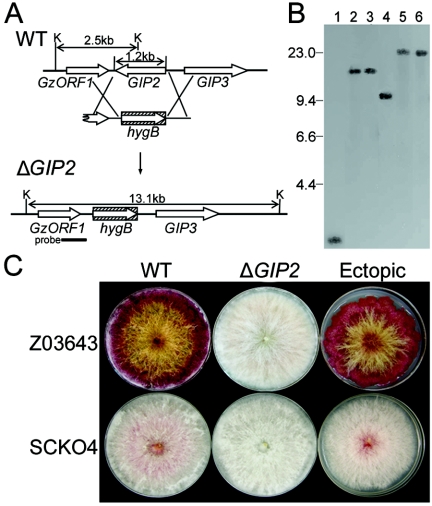
FIG. 2.
Targeted deletion of GIP2 from the genome of wild-type G. zeae strains Z03643 and SCKO4. (A) Deletion strategy. WT, genomic DNA of the wild-type strain Z03643; ΔGIP2, genomic DNA of the strain with GIP2 deleted; K, KpnI; hygB, hygromycin B resistance gene. The probe used for blot hybridization, which is amplified from genomic DNA of Z03643 with primers G2-3′f and G2-3′r (Table 1), is indicated by a thick bar. (B) Gel blot of KpnI-digested genomic DNAs from ΔGIP2 strains, hybridized with the probe. Lanes 1 and 4, Z03643 and SCKO4, respectively; lanes 2 and 3, the ΔGIP2 strains of Z03643 (Tzg2-1 and Tzg2-2, respectively); lanes 5 and 6, the ΔGIP2 strains of SCKO4 (Tsg2-1 and Tsg2-2, respectively). The sizes of λDNA standards (in kilobases) are indicated on the left of the blot. (C) Pigmentation of transformants of Z03643 and SCKO4. WT, wild-type strains; ΔGIP2, the GIP2-deleted strains Tzg2-1 and Tsg2-1; Ectopic, transformants carrying ectopic vector integrations (Tzg2-5 and Tsg2-8).