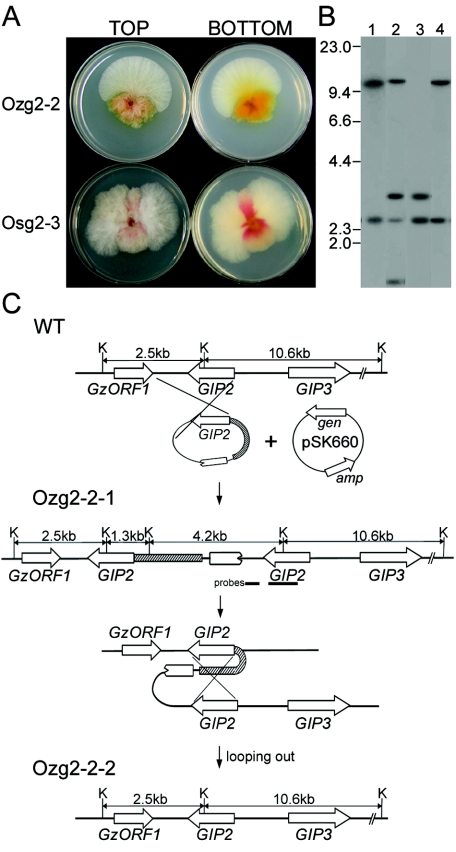
FIG. 6.
Overexpression of GIP2 in wild-type G. zeae strains Z03643 and SCKO4. (A) Pigmentation of transgenic strains. The upper and lower plates in each panel indicate transgenic strains carrying the heterologous GIP2, Ozg2-2, and Osg2-3 derived from Z03643 and SCKO4, respectively. (B) DNA gel blot of transformants derived from wild-type strains. Lane 1, Z03643; lanes 2 and 3, Ozg2-2-1 probed with GIP2 and a 3′ flanking region of GIP2, respectively; lane 4, Ozg2-2-2, probed with GIP2. The sizes of λDNA standards (in kilobases) are indicated on the left of the blot. (C) Overexpression strategy. WT, genomic DNA of Z03643; Ozg2-2-1, genomic DNA from mycelia of the highly pigmented original transformant Ozg2-2; Ozg2-2-2, genomic DNA from the wild-type sector from Ozg2-2; pSK660, a vector used for cotransformation; K, KpnI; Pb-tub, promoter region of the β-tubulin gene from Z03643; gen and amp, genes conferring resistance to geneticin and ampicillin, respectively. The probes of GIP2 and the 3′ flank of GIP2, which are amplified from genomic DNA of Z03643 with primer pairs G2-for and G2-rev and G2-3′f and G2-3′r, respectively (Table 1), are indicated by thick bars. GzORF1 and GIP3 are indicated by open arrows.