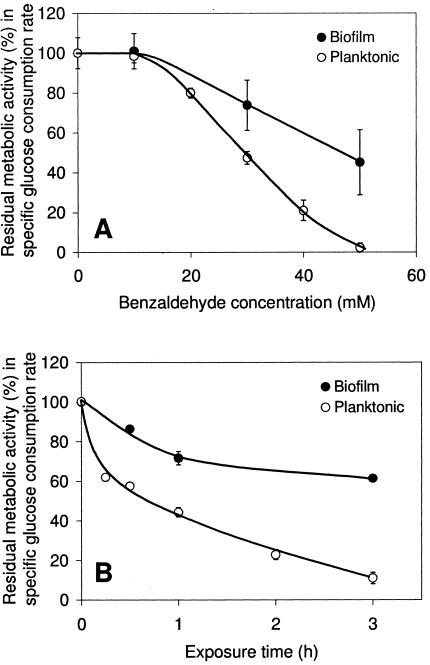
FIG. 3.
Quantitative analysis of benzaldehyde toxicity. Residual metabolic activity was measured by the specific glucose consumption rates of 3-day-old Z. mobilis biofilms and 24-h planktonic cultures after 1 h of exposure to different benzaldehyde concentrations (A) and after exposure to 30 mM benzaldehyde for up to 3 h at 30°C (B). Samples exposed to benzaldehyde for less than 3 h were preincubated in MES-buffered saline before benzaldehyde exposure to provide a total incubation time of 3 h. One hundred percent residual activity corresponded to the specific glucose consumption rate of control cultures exposed to MES-buffered saline without benzaldehyde, which was on average 30 mmol glucose mg total protein−1 h−1. The error bars indicate the sample standard deviations of results from independent cultures (n ≥ 4 for panel A and n ≥ 2 for panel B).