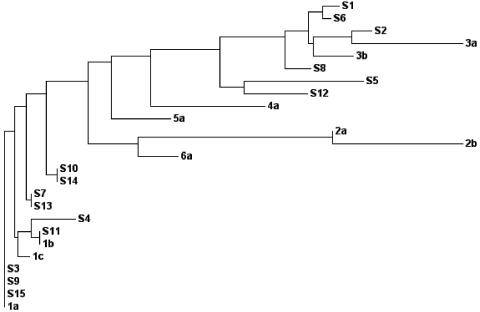
FIG. 2.
Phylogenetic analysis of the Indian isolates using the 5′ UTR sequences. Shown is a phylogenetic tree demonstrating the genetic relationships of different patient samples with standard HCV isolates based on the nucleotide identity of the 5′ UTR (nucleotides 70 to 310). The values of genetic distances between isolates are as follows: S1, 0.00278; S6, 0.00139; S2, 0.00313; 3a, 0.01771; 3b, 0.00635; S8, 0.00415; S5, 0.01904; S12, 0.01013; 4a, 0.01825; 5a, 0.00939; 2a, 0.00000; 2b, 0.02083; 6a, 0.00638; S10, 0.00000; S14, 0.00000; S7, 0.00000; S13, 0.00000; S4, 0.00706; S11, 0.00000; 1b, 0.00000; 1c, 0.00196; S3, 0.00000; S9, 0.00000; S15, 0.00000; and 1a, 0.00000.