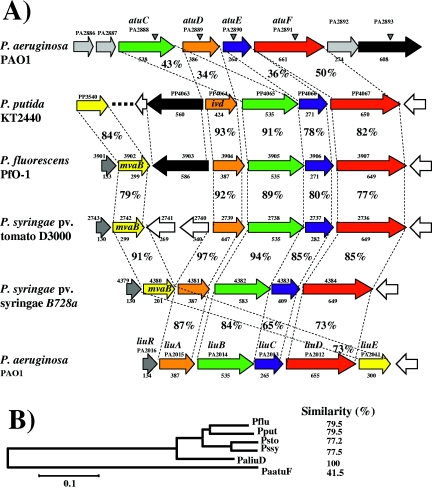
FIG. 2.
Sequence analysis of products encoded in the atu and liu gene clusters. (A) Genetic arrangement of the atu/liu homolog clusters from Pseudomonas species. The species and strain names are shown at the left. ORF arrangement and transcription direction are shown by arrows. Locations of transposon insertions in the P. aeruginosa mutants are indicated with shaded arrowheads. Numbers above arrows show the ORF number assigned in the respective genome sequencing project. Identified genes are also shown. The amino acid number of the ORF is indicated below the arrows. Corresponding ortholog proteins are indicated by the same color. Orange, LiuA; green, LiuB; blue, LiuC; red, LiuD; yellow, lyase (LiuE); black, PA2893.The percentages of amino acid identity between upper and lower ORFs are indicated. (B) Phylogenetic tree of the Atu/Liu homolog proteins of Pseudomonas species. The amino acid sequences of LiuABCD and AtuDCEF were put together as one sequence and aligned with the homologous sequences from the strains indicated. The alignment was done using the Clustal W software, and the tree was done by the neighbor joining in the Mega2 software with a bootstrap of 1,000 replicates. The numbers indicate the percent similarities between the amino acids sequences aligned. Pflu, P. fluorescens PfO-1; Pput, P. putida KT2440; Psto, P. syringae pv. tomato D3000; Pssy, P. syringae pv. syringae B728a; PaatuF, P. aeruginosa PAO1 atu cluster; PaliuD, P. aeruginosa PAO1 liu cluster. The evolutionary distance scale bar is shown at the bottom.